Connecting to Modbus Device
Connect to a Modbus Device
This driver requires the OPC UA module to be installed and enabled. If the module is missing or disabled, the device will fault with a “Missing Dependency” error on the Platform System > Modules page.
-
On the Gateway, go to Connections > Devices > Connections.
-
Click Create Device Connection +.
-
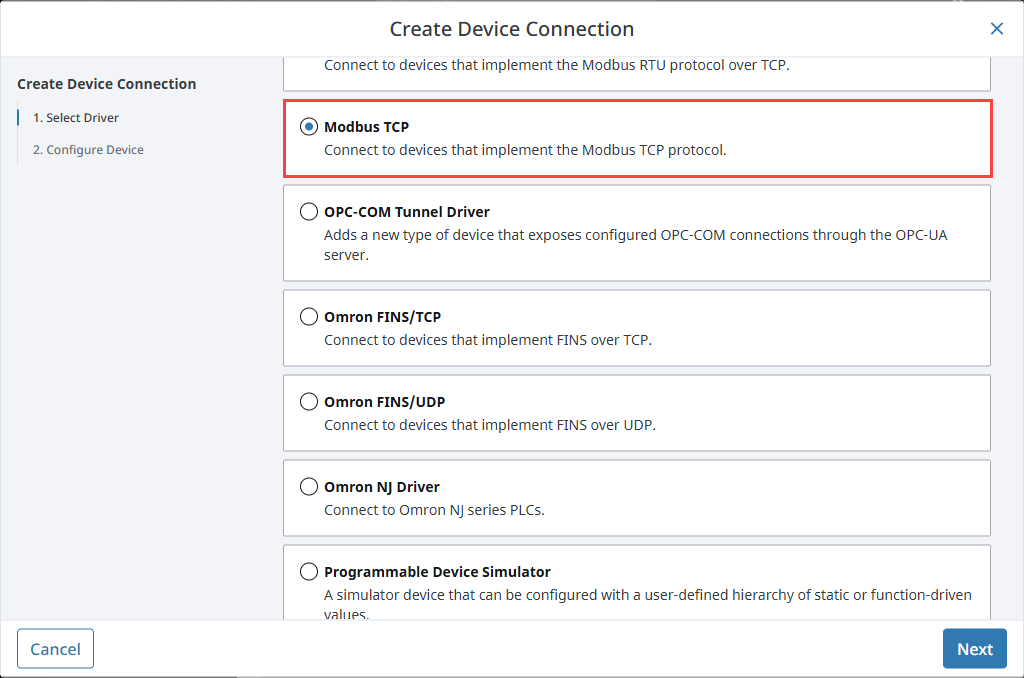
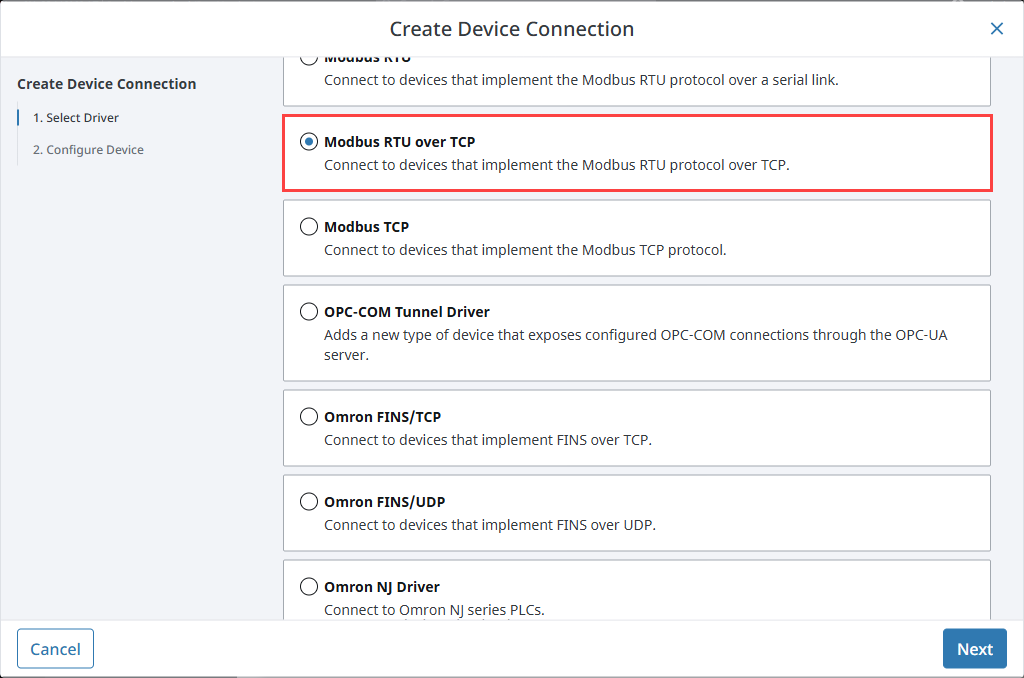
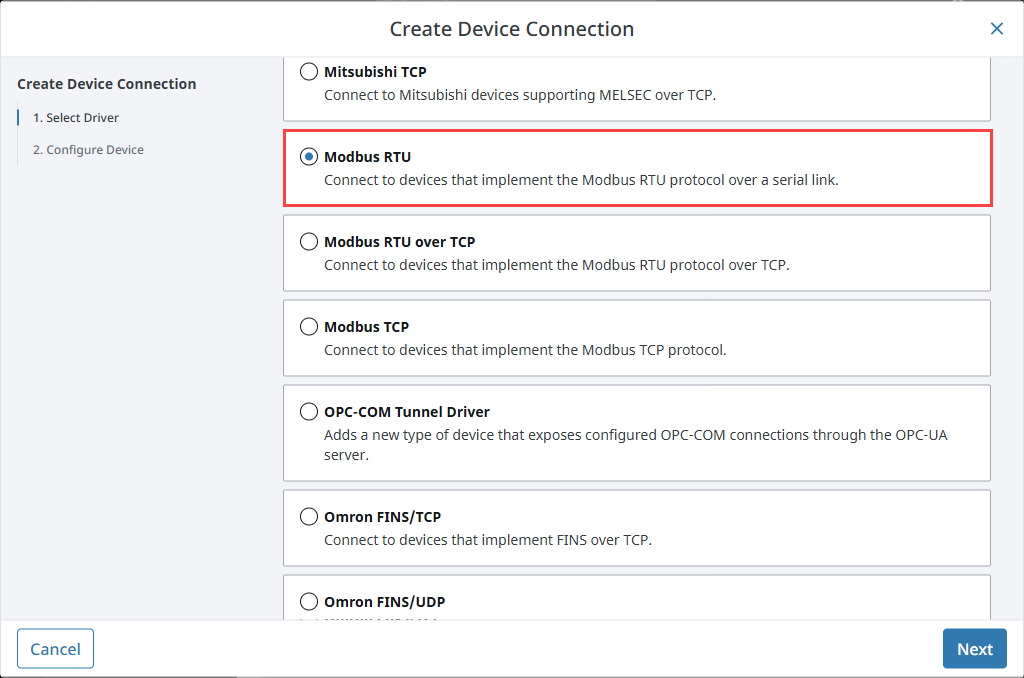
Choose a Modbus driver from the list and click Next:
-
Modbus TCP for devices that support native Modbus TCP/IP.
-
Modbus RTU over TCP for devices that encapsulate RTU messages inside TCP packets.
-
Modbus RTU for serial RTU communication.
-
-
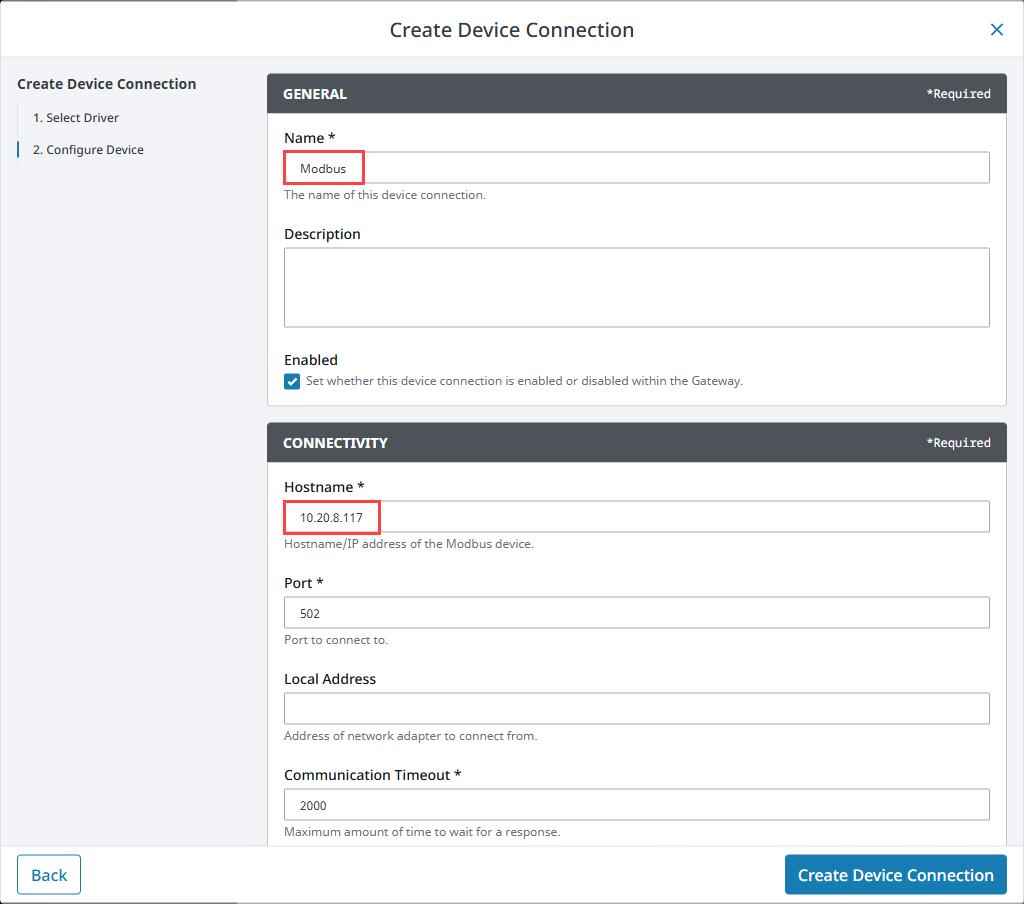
On the Configure Device screen, enter the required fields:
-
Name: Modbus
-
Hostname (TCP and RTU over TCP): IP address of the device (e.g., 10.20.8.117)
-
Serial Port (RTU): Serial port path (e.g., COM1)
-
-
Click Create Device Connection.
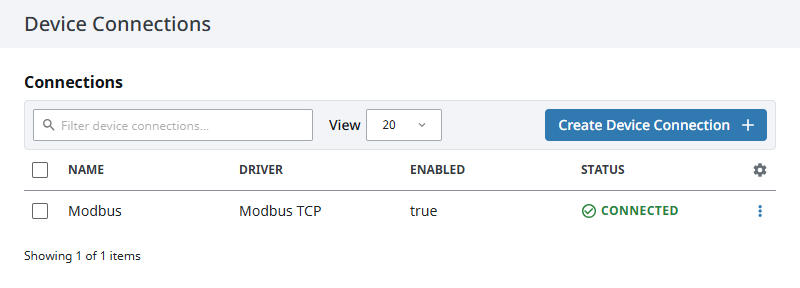
The device will be listed now on the Connections page. The status will initially show Disconnected, but will move to a Connected state.
Modbus devices do not support tag browsing. To access tags, you must manually define addresses in the Tag Browser or configure mappings using the Modbus Addressing and Modbus Address Mapping pages.
Modbus Protocol Support
The Modbus driver can connect to any device that supports the Modbus protocol via Ethernet or serial. Only one Modbus device should be added per IP address in the Ignition Device List. For Modbus Gateways that route to multiple devices, use separate unit IDs per device, either in the tag path or via the address mapping page.
Supported Function Codes
| Function Name | Code | Hex |
|---|---|---|
| Read Coils | 01 | 0x01 |
| Read Discrete Inputs | 02 | 0x02 |
| Read Holding Registers | 03 | 0x03 |
| Read Input Registers | 04 | 0x04 |
| Write Single Coil | 05 | 0x05 |
| Write Single Register | 06 | 0x06 |
| Write Multiple Coils | 15 | 0x0F |
| Write Multiple Registers | 16 | 0x10 |
| Mask Write Register | 22 | 0x16 |
Device Connection Settings
General
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | A user-defined name for the device. This name appears in OPC item paths and the Devices list. Name must begin with an underscore or a letter, and cannot include special characters. |
| Description | Optional description to help identify the device. |
| Enabled | When selected, the device is active and available for use. |
Connectivity – Modbus TCP / RTU over TCP
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Hostname | Specifies the IP address of the Modbus device or TCP Gateway. |
| Port | Defines the TCP port used by the device. The default is 502. |
| Local Address | Specifies the IP address of the local adapter to bind from. Leave this blank to allow automatic selection. |
| Communication Timeout | Sets the time, in milliseconds, to wait for a response before the request is considered failed. |
Connectivity – Modbus RTU
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Serial Port | Specifies the name of the serial port (for example, COM1). |
| Bit Rate | Sets the bit rate used for the serial connection. |
| Data Bits | Defines the number of data bits in the message frame. |
| Parity | Sets the parity configuration for serial communication. |
| Stop Bits | Defines the number of stop bits used in the frame. |
| Handshake | Specifies the flow control method for the serial connection. |
| Communication Timeout | Sets the time, in milliseconds, to wait for a response before the request is considered failed. |
| RS-485 Mode | Enables RS-485 mode instead of the default RS-232. |
Request Optimization
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Max Holding Registers per Read Request | Changed in 8.3.1 Specifies the maximum number of holding registers allowed per read request. The default is 125. |
| Max Holding Registers Per Write Request | New in 8.3.1 Specifies the maximum number of holding registers allowed per write request. The default is 123. |
| Max Input Registers per Request | Specifies the maximum number of input registers to read per request. The default is 125. |
| Max Coils per Request | Sets the maximum number of coils to read in a single request. The default is 2000. |
| Max Discrete Inputs per Request | Sets the maximum number of discrete inputs to read per request. The default is 2000. |
| Concurrent Requests | Defines the number of simultaneous requests the driver can issue. Not available for Modbus RTU. |
| Span Gaps | Specifies whether to span gaps in the address space to reduce the total number of requests. |
Write Request
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Allow Write Multiple Registers Request | Enables the use of function code 0x10 for writing multiple registers. Disable this option only if the device does not support it. |
| Force Multiple Register Writes | Forces the driver to use function code 0x10 for all multi-word register writes. |
| Allow Write Multiple Coils Request | Enables the use of function code 0x0F for writing multiple coils. Disable this option only if the device does not support it. |
Read Request
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Allow Read Multiple Registers Request | Enables reading registers in blocks instead of individually. Disable this option to read each register separately. |
| Allow Read Multiple Coils | Enables reading coils in blocks instead of individually. Disable this option to read each coil separately. |
| Allow Read Multiple Discrete Inputs | Enables reading discrete inputs in blocks instead of individually. Disable this option to read each input separately. |
Advanced
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Reconnect After Consecutive Timeouts | Forces the driver to reconnect after three consecutive timeouts. The default setting is true. |
| Reverse Word Order | Swaps the low and high words in 32-bit values. Enable this option if the data appears reversed. |
| Zero-based Addressing | Enables zero-based addressing. This is required by some Modbus implementations. |
| Max Retry Count | Sets the number of times the driver will retry a request after receiving a device error. The default is 1. |
String Handling
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Reverse String Byte Order | Reverses the byte order when reading string values. |
| Right Justify Strings | Pads string values to the right instead of the default left padding. |
| Read Raw Strings | Reads the full configured string length, including any null characters. |
