UDP and TCP Driver
Ignition’s UDP and TCP drivers allow communication with simple devices such as barcode scanners and scales. These drivers are not general-purpose PLC drivers, but lightweight tools for raw stream data over TCP or UDP.
They connect to one or more ports on a given IP address and receive any incoming data (ASCII characters, for example) as tag values. Both drivers can act as passive listeners, meaning they do not write or make requests unless configured to do so. This is ideal for devices that continually push data without expecting a poll/response.
The TCP driver supports an optional writeback capability, exposing writable tags to send data back to the device.
These drivers do not parse industrial protocols, but instead handle stream-oriented or delimited data only.
Structure in the Address Space
When you connect with these drivers, the device appears under the Devices folder of the OPC UA server with the configured name. Inside the device node, you will see:
- One folder per configured port
- Inside each port folder, one tag for the entire message
- Plus one tag for each configured field
For example, a device with four fields would expose five tags in its port folder.
Connecting to a Device
Instead of connecting directly to a PLC, these drivers connect to ports. The connected device must be configured to send data to those ports. You can configure multiple ports for a single device connection.
These drivers require the OPC UA module to be installed and enabled. If the module is missing or disabled, the devices will fault with a “Missing Dependency” error on the Platform > System > Modules page.
TCP Driver
The TCP driver can act as a passive receiver, or allow writes to be sent back to the device through tags if writeback is enabled.
Connecting to a TCP Device
-
On the Gateway, go to Connections > Devices > Connections.
-
Click Create Device Connection +.
-
Select TCP Driver from the list and click Next.
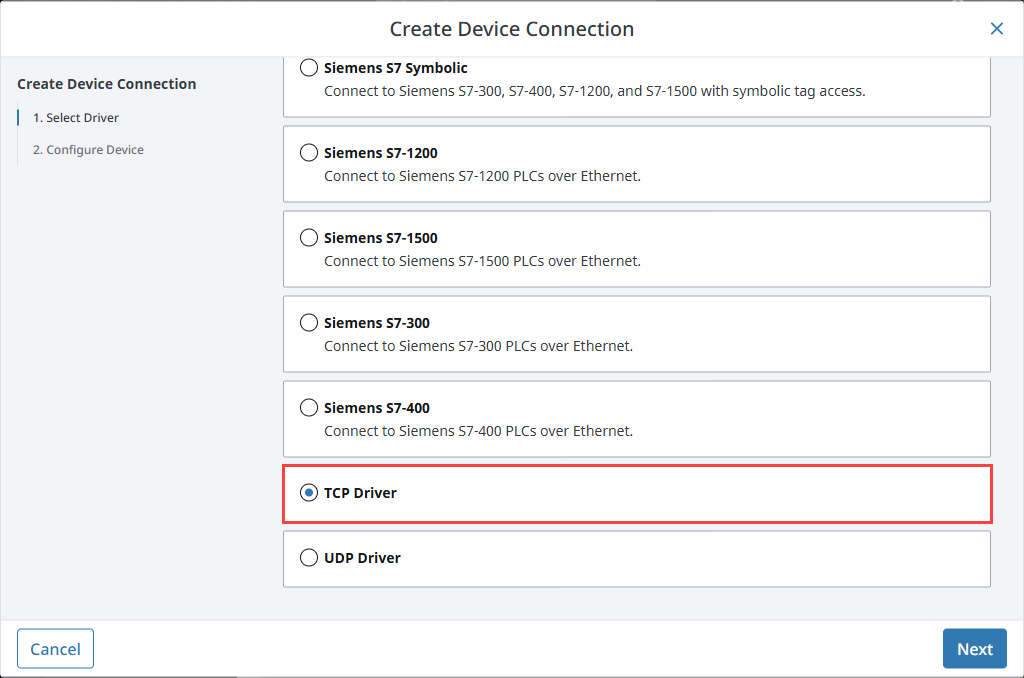
-
On the Configure Device screen, enter the required fields:
- Name: The desired name for the device (e.g., TCP)
- Port(s): The TCP port(s) to connect to, comma-separated. (e.g., 12345)
- Address: The IP address of the device (e.g., 10.20.3.45)
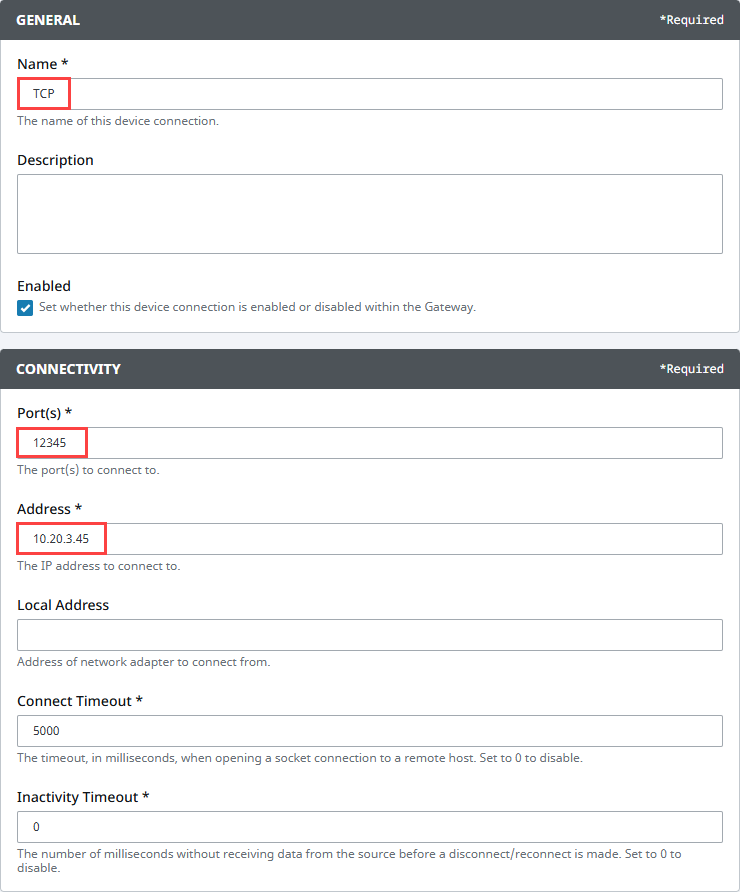
-
Click Create Device Connection.
The device will be listed now on the Connections page. The status will initially show Disconnected, but will move to a Connected state.
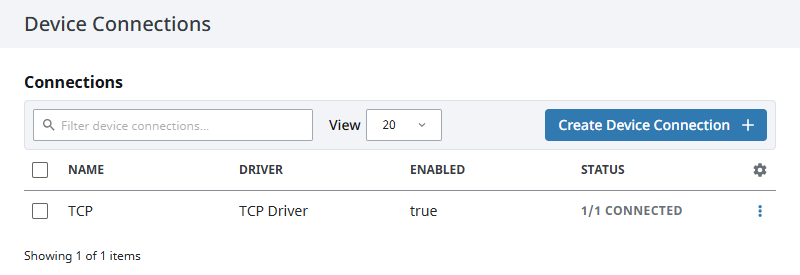
TCP Device Settings
General
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | A user-defined name for the device. This name appears in OPC item paths and the Devices list. Name must begin with an underscore or a letter, and cannot include special characters. |
| Description | Optional description to help identify the device. |
| Enabled | When selected, the device is active and available for use. |
Connectivity
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Port(s) | Specifies the TCP port or ports to connect to. Multiple ports can be entered as a comma-separated list. |
| Address | Specifies the IP address of the device to connect to. |
| Local Address | Defines the local IP address to bind from, if needed. |
| Connect Timeout | Sets the time, in milliseconds, to wait for a socket connection. A value of zero disables the timeout. |
| Inactivity Timeout | Sets the time, in milliseconds, of allowed inactivity before the connection is reset. A value of zero disables the timeout. |
Message
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Message Delimiter Type | Defines how message boundaries are determined. Options include Packet Based, Character Based, or Fixed Size. |
| Message Delimiter | Specifies the characters or length used to identify the end of a message, depending on the delimiter type. |
| Field Count | Sets the expected number of fields in each message. |
| Field Delimiter | Specifies the characters used to separate fields within a message. |
Writing
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Writeback Enabled | Enables writable tags to send data to the device. |
| Writeback Message Delimiter | Specifies the delimiter that signals the end of a message during writeback operations. |
| Write Timeout | Sets the time, in milliseconds, to wait for a write to complete. The default value is 5000. |
TCP Tags
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Last Receive Time | Displays the timestamp of the last message received from the device. |
| Message | Shows the string representation of the last received message. |
| MessageBytes | Displays the binary (byte-level) representation of the last received message. |
| Writable | Allows writing of string data to the device if writeback is enabled. |
| WritableBytes | Allows writing of binary data to the device if writeback is enabled. |
UDP Driver
The UDP driver is a passive listener only. It does not send data back to the device and is well-suited for broadcast-type devices.
Connecting to a UDP Device
-
On the Gateway, go to Connections > Devices > Connections.
-
Click Create Device Connection +.
-
Select UDP Driver from the list and click Next.
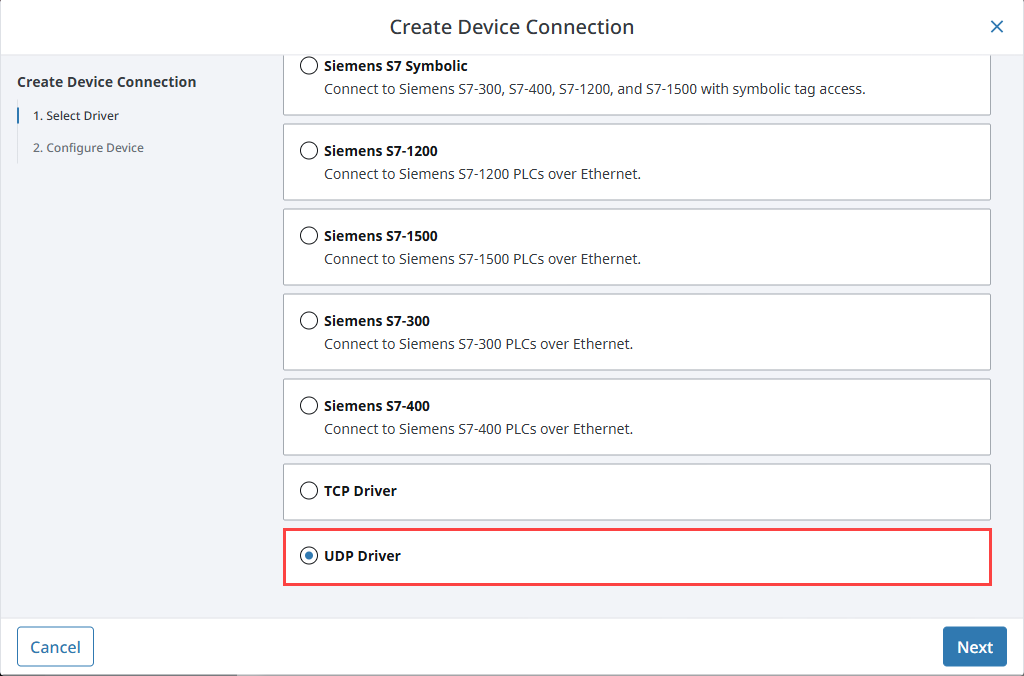
-
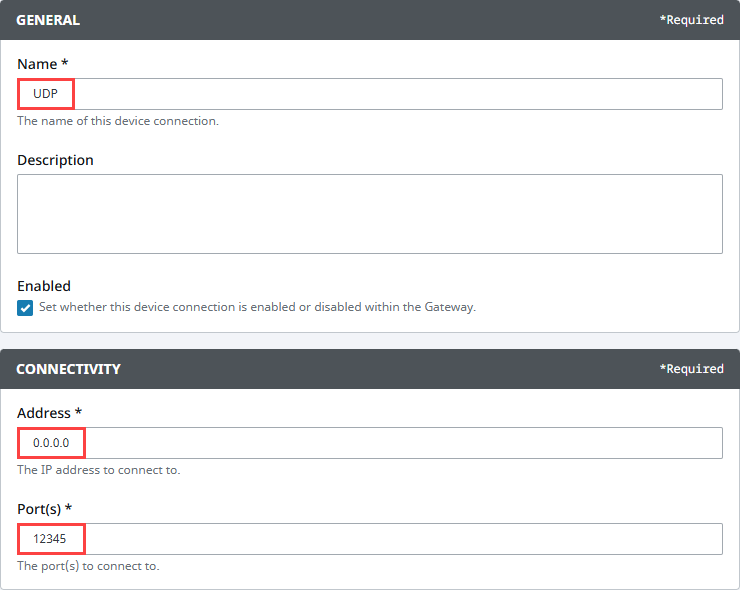
On the Configure Device screen, enter the required fields:
- Name: The desired name for the device (e.g., UDP)
- Port(s): The UDP port(s) to connect to, comma-separated. (e.g., 12345)
- Address: The IP address of the device (e.g., 0.0.0.0 to listen on all interfaces)
-
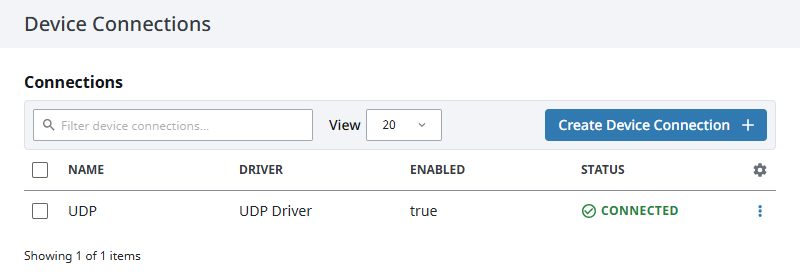
Click Create Device Connection.
The device will be listed now on the Connections page. The status will initially show Disconnected, but will move to a Connected state.
UDP Device Settings
General
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | A user-defined name for the device. This name appears in OPC item paths and the Devices list. Name must begin with an underscore or a letter, and cannot include special characters. |
| Description | Optional description to help identify the device. |
| Enabled | When selected, the device is active and available for use. |
Connectivity
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Address | Specifies the IP address that the device will listen on. |
| Port(s) | Defines the UDP port or ports to listen on. Multiple ports can be entered as a comma-separated list. |
Message
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Message Delimiter Type | Defines how message boundaries are determined. Options include Packet Based, Character Based, or Fixed Size. |
| Message Delimiter | Specifies the characters or length used to identify the end of a message, depending on the delimiter type. |
| Field Count | Sets the expected number of fields in each message. |
| Field Delimiter | Specifies the characters used to separate fields within a message. |
UDP
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Message Buffer Size | Sets the size of the message buffer, in bytes. |
| Multicast | Enables multicast mode for receiving messages. |
UDP Tags
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Last Receive Time | Displays the timestamp of the last message received from the device. |
| Message | Shows the string representation of the last received message. |
| MessageBytes | Displays the binary (byte-level) representation of the last received message. |
Message Delimiters
Some devices use control characters to signal the end of a message. Tag values update no faster than the scan class they use. If messages arrive more quickly than the scan class, Ignition will drop them. Typical reliable scan rates are 100–200 ms, though TCP can theoretically scan down to 25 ms, and UDP depends heavily on network conditions. You can specify these in the driver settings.
| Characters | Description |
|---|---|
| \t | Represents a tab character. |
| \b | Represents a backspace character. |
| \n | Represents a newline character. |
| \r | Represents a carriage return character. |
| \f | Represents a form feed character. |
If tags show unexpected bad quality, check your delimiter and field count settings. Mismatches will result in BAD_CONFIG_ERROR.
