Secrets Management
💡Have feedback for this page? Let us know on the IA Forum.
Secrets Management is the practice of securely storing and managing secrets on behalf of a user or system who owns and controls them. Common secrets include passwords, private keys, credentials, and access tokens. Ignition's Secrets Management system encrypts these secrets through built-in implementation. For a more robust setup, you can further customize your Ignition Secrets Management system from the default and create Secret Providers to store confidential secrets.
The process built into the Ignition platform is referred to as embedded secrets, while referenced integration is available through Secret Providers. Currently, only an internal Secret Provider is available to enable the referenced secrets functionality.
Establishing a Secrets Management System
Fresh Ignition installations are packaged with a default encryption key that is used to encrypt all secrets on the Gateway and provide the foundation for a more complex Secrets Management system. Although the default encryption key configuration is all that's required to set Gateway System Secrets, it is recommended to customize both your Root Key and create Encryption Key Sets, as the single default key matches every Ignition installation.
You must opt in to the Secrets Management system complete functionality to customize the Secrets Management system and secure features, like customizing your keys, creating key sets, or otherwise enhancing your system with additional security layers. This is because it will be the user's responsibility to maintain the system once it has been customized. Refer to the Secrets Management Key CLI Tool section for more information about opting in, customizing your keys, and performing other Secrets Management tasks.
If you choose to establish a Secrets Management system, you are provided new keys and files that make up the layers of the Secrets Management system, beginning with the default Root Key and Encryption Key set. As described for the default setup, Encryption Keys Sets will still serve as the first step used to encrypt all secrets on the Gateway. However, instead of a single shared Encryption Key, you'll now have three keys that are all unique to you. The reason they are provided as a set is so that they can be rotated for an additional security measure. The Encryption Key Set is stored securely as a kek.json file, and requires the Root Key to decrypt. Similarly, the Root Key is encrypted and stored as a root.json file. The final component you need to establish for your Secrets Management system is a unique environment password. This is delivered in a file and is used to decrypt the root.json file so the Root Key is usable.
To maintain security, the environment password is not saved within the system by default. Access to the environment password is possible through the use of environment variables, which make sure Ignition has the ability to decrypt your secrets.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
IGNITION_ROOT_KEY_PASSWORD_FILE | The path to a file in a folder with the root key password. |
IGNITION_ROOT_KEY_PASSWORD | The custom key to start the Gateway. |
It is essential to keep track of your environment password because without it nothing can be decrypted and your system will fail when attempting to verify the the Secrets Management system, such as on startup. If the Gateway cannot find the environment password, or if the password is invalid, there is an option on the Gateway or in command line utility to attempt to unseal the custom Root Key with the environment password manually. This option is available in situations where the password is held by company personnel instead of being stored digitally.
If you are upgrading from a version without a customized Secrets Management system configured, it will be treated as a fresh install. If you are upgrading with a Secrets Management system configured, it will be detected and maintained through the upgrade process.
Make sure that the root and KEK JSON files are applied to both the Master and Backup nodes in a redundant configuration. If not, the embedded secrets and Internal Provider secrets encrypted on one will not decrypt on the other.
Gateway Startup Example
The Secrets Management system is verified on each Gateway startup, regardless of how many, if any, secrets are configured. This is to ensure an encryption key set is available for both decrypting existing secrets and for encrypting any new or changed secrets during the lifetime of a running Gateway. The following steps describe this process in simplified terms:
- The
/data/config/ignition/keysdirectory must be present with both theroot.jsonandkek.jsonfiles. - The environment password is located and loaded through the environment variables, and is able to decrypt the
root.jsonfile. - The Root Key is able to decrypt the
kek.jsonfile.
Once the system confirms the Encryption Key Set can be decrypted and used to decrypt the Gateway secrets, the Secrets Management system is confirmed and the Gateway startup process moves on to the next task.
If the /data/config/ignition/keys directory doesn't exist, but the IGNITION_ROOT_KEY_PASSWORD or IGNITION_ROOT_KEY_PASSWORD_FILE environment variables are set, a new Root Key and custom Encryption Key set will be generated on startup so the startup process can continue.
Secrets Management Key CLI Tool
A Secrets Management Key CLI Tool is shipped with Ignition for users to be able to directly manage secret keys and run scripts from the command line, just like with the gwcmd and ignition.sh files. The Secrets Management Key CLI Tool exposes basic commands like generating, resetting, removing, and rotating keys.
- On Windows, use
ignition-secrets-tool.bat. - On *NIX, use
ignition-secrets-tool.sh.
See the Secrets Management Key CLI Tool page for more information on the available commands.
Configuring Gateway System Secrets
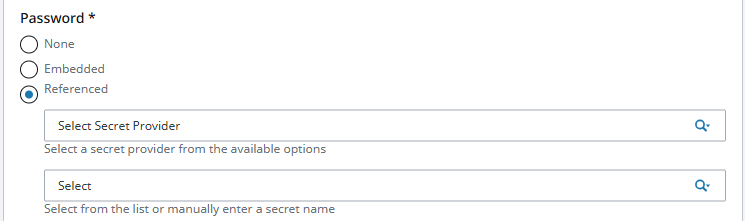
The Secrets Management system replaces standard password and re-type password fields on the Gateway to offer the following three options when creating or editing devices, profiles, and system configurations that require security:
-
None: Confirms no password is needed for the corresponding Gateway system. Although always visible, this option will be grayed out if a secret is required.
-
Embedded: Displays a field to enter a secret. By default the characters will be hidden, but they can be made visible using the SHOW option. Once the secret is saved, it is encrypted and cannot be made visible to any user. An Update Password option will appear in case the password needs to be changed. This option replaces standard password and re-type password fields.
-
Referenced: Displays two new fields for choosing a Secret Provider and secret name for the corresponding Gateway system to reference. Although always visible, this option is only available for configuration when a Secret Provider exists.
Embedded Secrets
Secrets that are stored and managed internally in Ignition are considered to be embedded, as they don't depend on any external secrets management solution. Instead, embedded secrets use Ignition's encryption system.
Once an embedded secret is entered and saved, it is automatically encrypted. These secrets can only be exposed using an encryption key. Upon initial installation, you'll be given default encryption keys. For increased security, it's recommended to customize these encryption keys.
Using Secret Providers
Secret Providers offer a way for users to utilize Ignition as a Secrets Management service through referenced secrets. While the use of Secret Providers is not equivalent to incorporating a dedicated Secrets Management system, they can offer a solution to manage many secrets if no other option is otherwise configured.
Secret Providers now support the use of system functions to encrypt, decrypt, and access stored secret data. Refer to the system.secrets page for more information on using each function.
Internal
With an Internal Secret Provider, secrets are managed by Ignition using an embedded secrets management strategy. All secrets within this provider are stored as files on the Gateway and referenced by an assigned name. This means secrets shared by multiple configs can reference the same name to facilitate re-use.
It is recommended to use different secrets for each system or connection requiring one.
Provider Properties
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name for the Internal Secret Provider. |
| Description | A description of the Secret Provider. [optional] |
| Enabled | Determines whether the Secret Provider is enabled or disabled within the Gateway. |
Remote
A Remote Secret Provider creates a link to a Secret Provider on a remote Gateway over the Gateway Network. Once connected, Ignition can list and read secrets. Remote Secret Providers service settings default to deny access and must be manually updated to allow access. The Secret Provider Access settings can be updated within the corresponding Security Zone's Manage Policy panel Secret Provider Access section.
Provider Properties
General
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name for the Remote Secret Provider. |
| Description | A description of the Secret Provider. [optional] |
| Enabled | Determines whether the Secret Provider is enabled or disabled within the Gateway. |
Remote Gateway
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| Gateway Name | The remote Ignition Gateway server from which to fetch secrets. |
| Secret Provider | The Secret Provider on the remote Ignition Gateway server from which to fetch secrets. |
Creating a Secret Provider
To create a Secret Provider, complete the following steps. This example creates an Internal Secret Provider.
-
Access your Gateway and navigate to Platform > Security > Secret Provider.
-
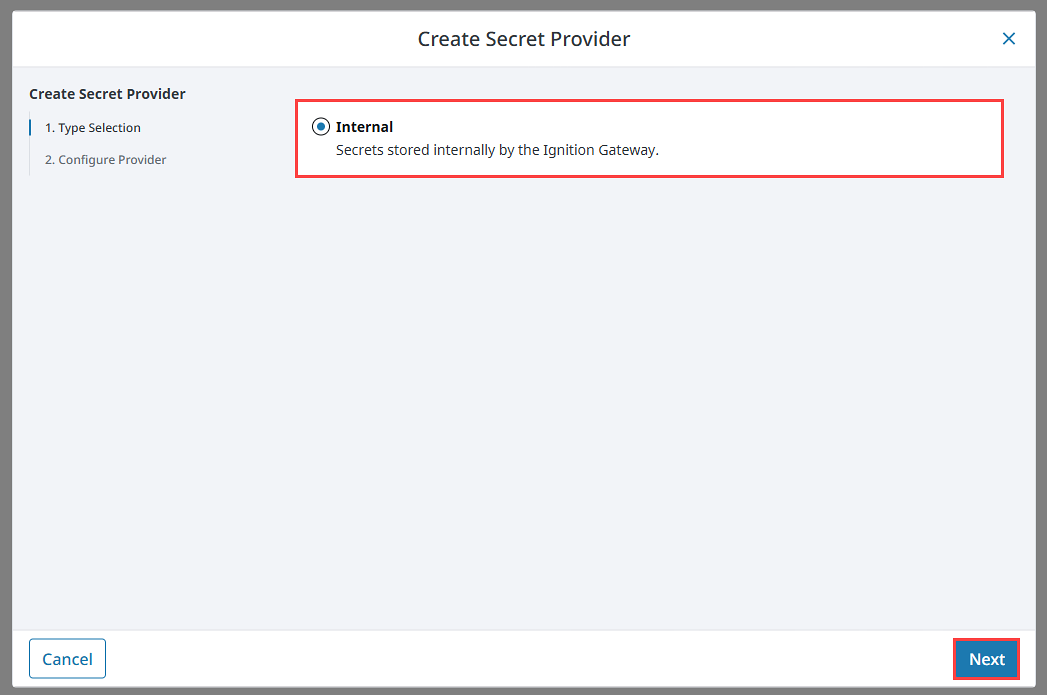
Select Create Secret Provider +. The Create Secret Provider form will appear.
-
The Create Secret Provider form will appear with Internal selected, click Next.
-
Enter a name for your Secret Provider, and a description as desired. The Secret Provider will be enabled by default. The provider was named Internal_Provider for this example.
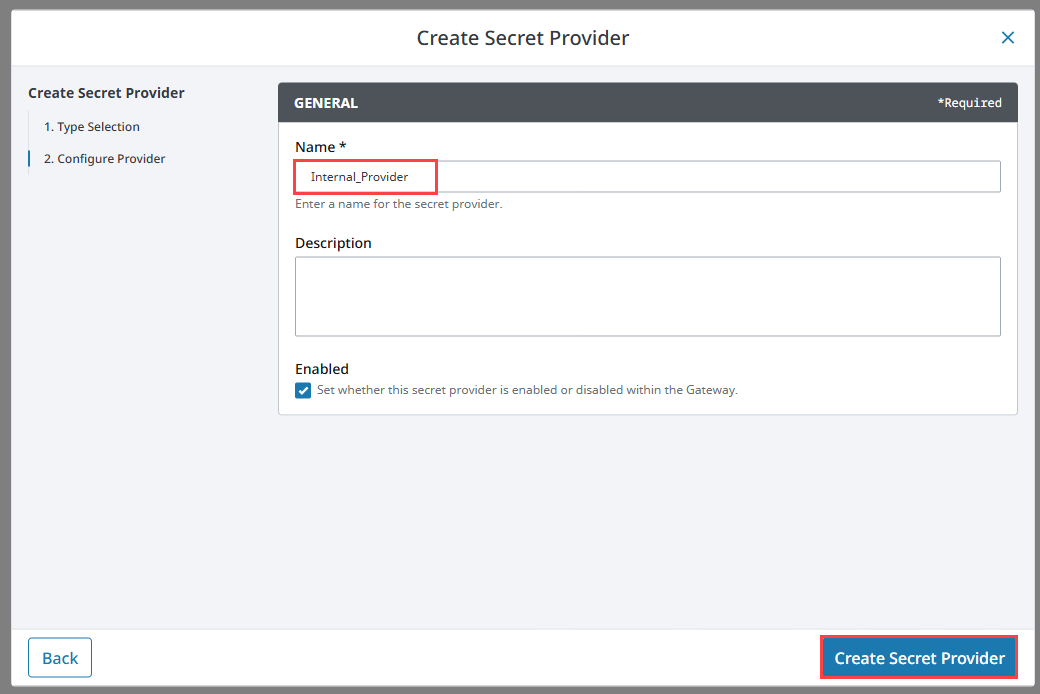
-
Click Create Secret Provider.
Your Secret Provider will now be displayed on the Secret Providers page where you can expand the three dots menu to make any further configurations relevant to your provider.
If you already have embedded passwords configured for various systems and decide to set up a Secret Provider later, you can simply update the password selection for that secret from embedded to referenced in the Edit panel on the Gateway page.
Managing Secrets
Secrets within a Secret Provider are added and updated on the Manage Secrets panel. Click the three dots menu for the Secret Provider and select Manage Secrets to access the Manage Secrets panel. Note that the Manage Secrets option is only available for Internal Secret Providers as secrets cannot be created with Remote Secret Providers.
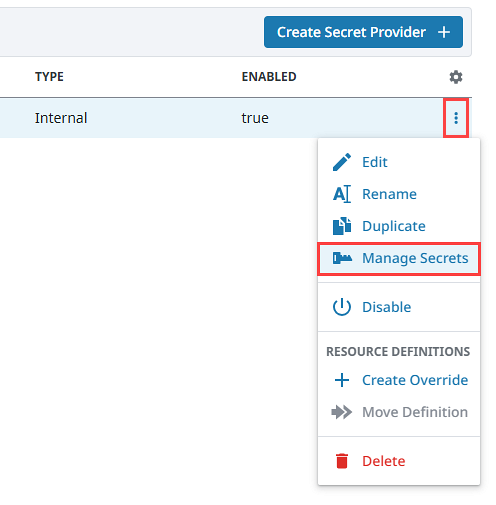
From here, you can select Create Secret + to access the Create Secret form. Now, simply enter a name for the secret and the secret value. The Description field is optional. Once added, an encrypted secret value is created. This value cannot be read from the Gateway.
If you need to update an existing secret value, click the three dots menu for the secret and select Edit where you'll see the Reset Secret Value option. While you enter a new secret value, you'll have visibility to the value. However, once the new value is saved, it will once again be encrypted and hidden.
Secret Properties
General
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| Secret Name | The name of the secret. |
| Description | The description of the secret. [optional] |
Secret Value
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| Secret Value | The value to store for this secret. Upon creation, the secret value will be encrypted and cannot be read again within the Gateway. |