Ignition Redundancy
Ignition redundancy supports a 2-node system, meaning there are two copies of the Gateway running. One node is the master Gateway and the other is the backup Gateway or backup node. Unless otherwise configured through Backup Versions, the master node manages the configuration, then replicates it to the backup node.
Refer to the Updating or Patching a Redundant Ignition Pair Knowledge Base Article to learn more about updating redundant servers successfully.
When you have redundant systems in place, you can go to your Gateway and select Platform > System > Redundancy to view the system's status and events.
Redundancy Page Overview
This section breaks down the Redundancy page, describing each feature.
Metrics and Information
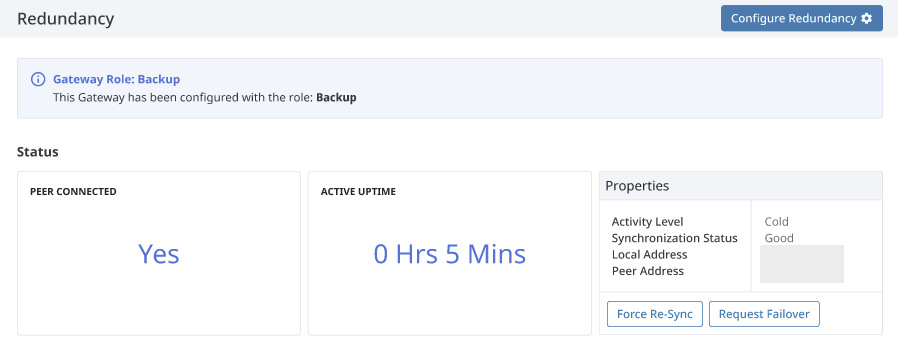
The top section of the Redundancy page for a backup Gateway gives information about the Gateway and your redundancy setup, including:
- Redundancy configuration settings
- The current Gateway's role in the Redundant pair
- If the Gateway has a peer connected
- The current node's uptime after failover
- Current redundancy settings
- Force re-sync and request failover options
The Request Failover option switches the active node in a redundant pair. Failover to the other redundant node is allowed if the nodes have different platform versions, which will allow attached clients to remain connected to at least one node during a redundant pair upgrade.
The following image is the Redundancy page from the master Gateway. Many features of the Redundancy page remain the same, with a few notable exceptions.
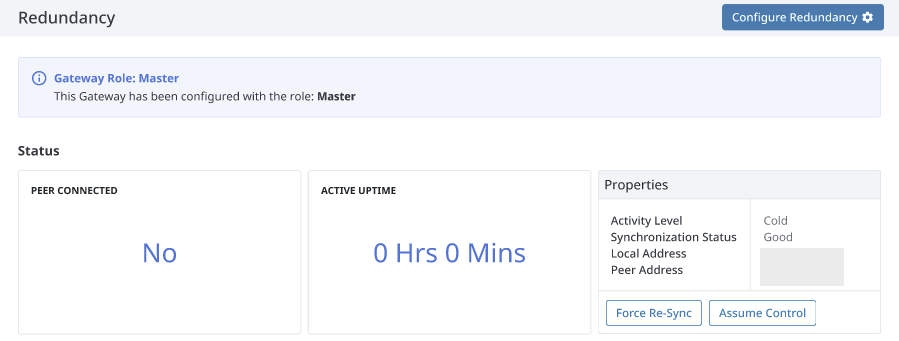
- The Role is different, reflecting the Gateway's role in the redundant pair.
- There is now an Assume Control option.
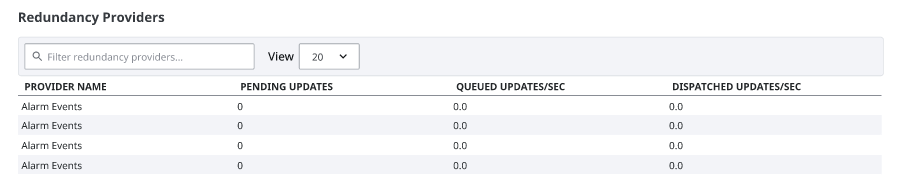
Redundancy Providers Statistics
The next section of the Redundancy page details metrics about applicable redundancy providers.
Data presented for Backup roles include:
- Provider Name: The name of the provider.
- Last Pull: Displays the time since the provider was last pulled.
- Last Pull Duration: The latest time duration (or how long it takes) for the Gateway to get data from the provider.
- Last Apply Duration: The latest time duration (or how long it takes) for the Gateway to apply the data received from the provider.
- Full Sync Needed?: Displays whether a full sync is needed. The Force Re-Sync button forces a full synchronization of the redundant configuration state. The backup node will be forced to restart.
- System Restart Required: Displays whether a system restart is needed.
Data presented for Master roles include:
- Provider Name: The name of the provider.
- Pending Updates: The number of updates waiting to be sent to the other node. If the other node is not connected, this number may grow continually.
- Queued Updates/sec: The number of updates per second over a 1 minute average that this redundant node has posted, which gives an indication of how quickly this node is posting updates.
- Dispatched Updates/sec: The number of updates per second over a 1 minute average that the other node has pulled, which gives an indication of how quickly the other node is asking for updates.
System Event Information
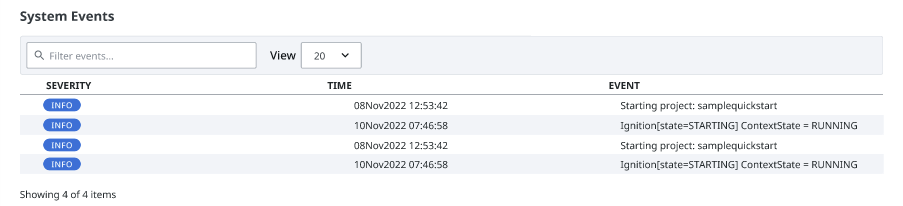
The third section of the Redundancy page displays a table that will log system events whenever a full sync is required, helping to establish a timeline of when full sync events were requested.
Information displayed in this table includes:
- How severe the system event was/is
- When the system event occurred
- The reason for the system event
Logging Activity
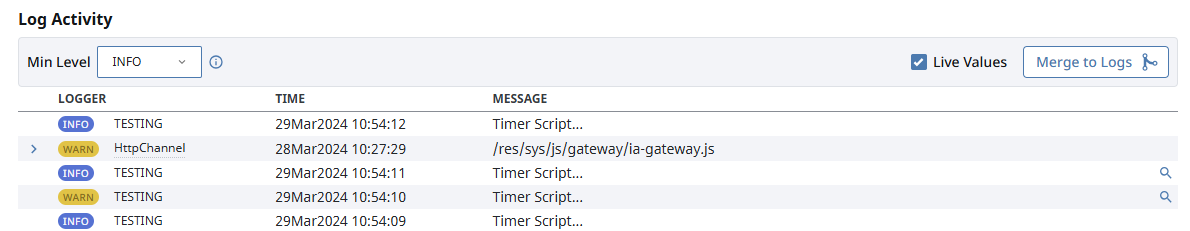
The final section of the Redundancy page shows logger activity and allows users to enable DEBUG and TRACE logs for a specific redundancy provider.
Features of the log activity table include:
- Minimum logging level. Options are:
- INFO
- DEBUG
- TRACE
- An option to merge logs to the main diagnostic log viewer
- The specified logger
- The log's timestamp
- The issue being logged
Node Communication
The master and backup nodes communicate over TCP/IP. Therefore, they must be able to see each other over the network, through any firewalls that might be in place. All communication goes from the backup to the master node over the Gateway Network (default port 8088 without SSL, port 8060 with SSL), so that port must allow TCP listening on the master machine.
Disabling the Gateway Network on a redundant master disables the same setting on the backup. The Enabled setting must be re-checked on both Gateways to successfully restore the connection. To allow this, the General Gateway Network settings can now be modified on a backup Gateway. Any other General Gateway Network settings changed on the backup will be overwritten with the master settings once the nodes are synced.
Configuration Synchronization
By default, the master node maintains the official version of the system configuration. This means that any changes made to the master Gateway are replicated on the backup Gateway. Additionally, the Designer only connects to the master node.
When changes are made on the master, they are queued up to be sent to the backup node. When the backup connects, it retrieves these updates, or downloads a full system backup if it is too far out of date. If the master node has modules that aren't present on the backup, they are sent across. Both types of backup transfers, data only and full, will trigger the Gateway to perform a soft reboot.
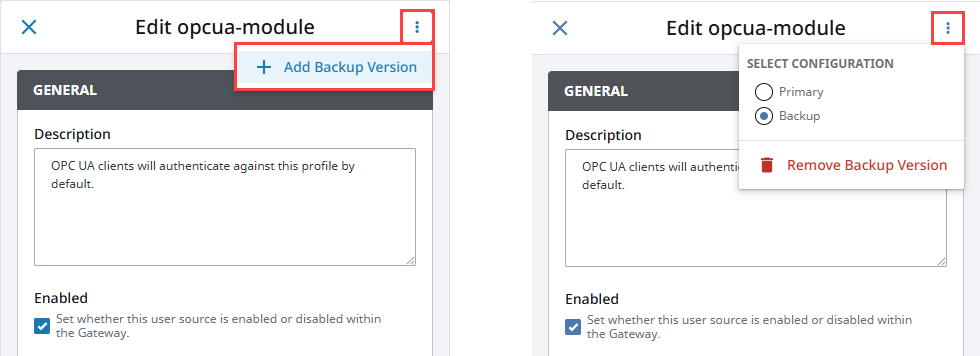
If you want any resource to have a different configuration on the backup Gateway, all you need to do is expand the three dots menu in the upper right-hand corner of that resource page or Edit panel, and select Add Backup Version. Changes saved on the Backup configuration will be applied to the backup Gateway and changes saved on the Primary configuration will be applied to the master Gateway.
Runtime State Synchronization
Information that is only relevant to the running state, such as current alarm states, is shared between nodes on a differential basis so that the backup can take over with the same state that the master had.
On first connection or if the backup node falls too far out of sync, a full state transfer is performed. This information is light-weight and does not trigger a Gateway restart.
After the master Gateway and backup Gateway reestablishes a redundancy connection, the backup Gateway will check if it has any conflicting data compared to the master Gateway's data. If the backup Gateway has instances of conflicting data, the backup Gateway will drop those instances in favor of the master Gateway's data.
The above behavior changes depending on if the Use Active Uptime to Resolve Conflicts property is toggled. If this property is toggled, the redundancy system will compare the master and backup nodes' active uptimes to each other, and use the data from the node with higher active uptime. This behavior can result in the master overwriting its own data with data from an active backup node.
Status Monitoring
Once connected, the nodes begin monitoring each other for liveliness and configuration changes. While the master is up, the backup runs according to the stand by activity level in the settings.
When the master cannot be contacted by the backup for the specified amount of time, it is determined to be down and the backup assumes responsibility. When the master becomes available again, responsibility is dictated by the recovery mode and the master either takes over immediately or waits for user interaction.
Historical Logging
Historical data presents a unique challenge when working with redundancy because it is never possible for the backup node to know whether the master is truly down or simply unreachable. If the master was running, but unreachable due to a network failure, the backup node becomes active and begins to log history at the same time as the master, who is still active.
In some cases this is OK because the immediate availability of the data is more important than the fact that duplicate entries are logged. But in other cases, it's desirable to avoid duplicates, even at the cost of not having the data available until information about the master state is available.
Ignition redundancy provides for both of these cases, with the backup history level, which can be either Partial or Full.
-
In Full mode, the backup node logs data directly to the database.
-
In Partial mode, however, all historical data is cached until a connection is reestablished with the master. At that time, the backup and master communicate about the uptime of the master, and only the data that was collected while the master was truly down is forwarded to the database.
Client Failover
Failover to the other redundant node is allowed if the nodes have different platform versions, which will allow attached clients to remain connected to at least one node during a redundant pair upgrade.
Vision Clients
All Vision Clients connect to the active node. When this system fails and is no longer available, they automatically re-target to the other node. The reconnection and session establishment procedures are handled automatically, but the user is notified that they have been transferred to a different node so that they can notify the system administrator that the system may need attention.
Perspective Sessions
Like Vision Clients, Perspective Sessions connect to the active node. When connection to the active node is lost, or the activity level of the Gateway changes from active, the session will simultaneously attempt to:
-
Re-establish the connection to the Gateway it was connected to, and check to make sure its activity level is active.
-
Monitor the backup Gateway. If the backup Gateway becomes reachable and active before the connection to the active Gateway can be re-established, the Perspective session navigates in the browser to the same project and page on the backup Gateway.
If your backup Gateway is not able to fail back over to the primary when the primary takes back control, turning off the Auto Detect HTTP Address property may resolve the issue. When the Auto Detect HTTP Address property is disabled, a public IP address that is reachable by both Gateways must be set.
