Editing Scan Classes
Adding and Editing Scan Classes
Adding and editing scan classes is really easy in the Designer once you understand how the different scan class modes work. It's just a matter of choosing which scan class mode you want to use for your Tag, and entering the properties for your scan class.
To Add and Edit a Scan Class
-
In the Tag Browser, click on the Timer icon (
) to open the Scan Class Editor window.
-
A list of already configured scan classes appear on the left side of the window, and configuration settings on the right. Click on a scan class to edit it, and to add a scan class, simply click the green + icon on the lower-left of the window.
-
For creating a new scan class, specify the Name of the scan class, and select a Mode: Direct, Driven, or Leased.
-
Enter the Slow, Fast, and Stale Timeout rates, as applicable. (Not all the rates are editable based on the type of scan class you are using).
-
If you're using a Driven scan class, enter the driving properties if they are applicable to the type of scan class you're using:
- Driving Tag - select the driving Tag from the dropdown list on the right side.
- Operator - determines how the Value property should be compared to the Driving Tag's value.
- Value - uses the Operator property to determine if the scan class should execute at the slow or fast rate.
- Execution Properties - mark the checkbox if this is a one-shot execution.
-
Enter Advanced Properties (optional)
- OPC Data Mode - dictates how the OPC values are obtained, by Subscription or Read.
- OPC Read After Write - mark the checkbox to enable read after write.
For more information on how to set up each scan class mode refer to Direct, Driven, Leased, and Driven One-shot sections.
A screenshot of the Scan Class Editor is shown below. Each Scan Class Editor property is described in detail in the table below.
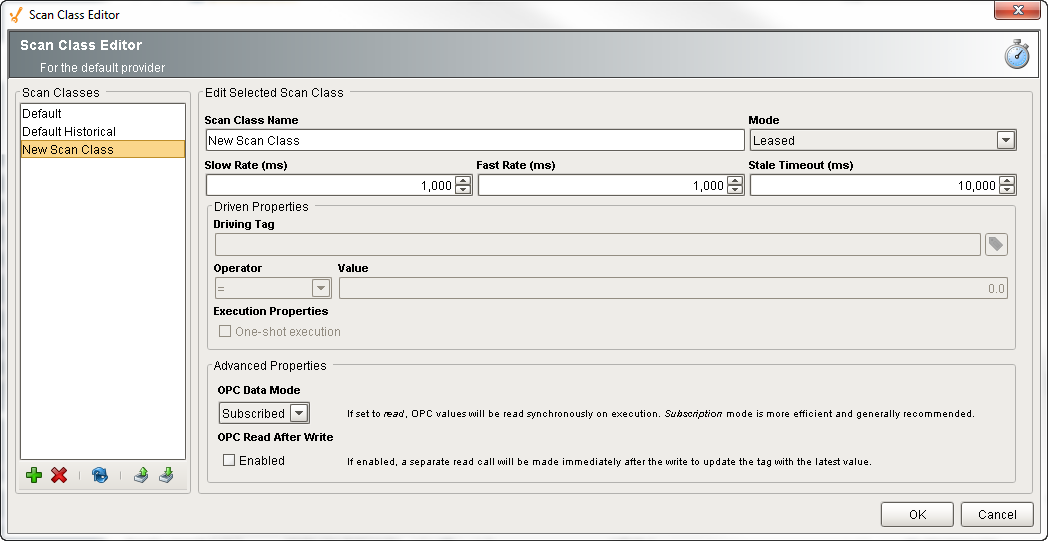
Scan Class Editor
Settings that edit a selected scan class.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Scan Class Name | Unique name of the scan class. |
| Mode |
|
| Slow Rate | Base update rate, specified in milliseconds, at which Tags will be executed. Note: If the rate is set to 0, the scan class will not be executed. It is common for leased and driven modes to use 0 as a slow rate in order to achieve an on/off effect. |
| Fast Rate | Used by the Driven and Leased modes, this is the faster rate that the Tags will be executed at when those modes are active. Note: If the rate is set to 0, the scan class will not be executed. |
| Stale Timeout | How long to wait before the Tags in the scan class are determined to be stale (not running). This is calculated off of the last expected execution time of the scan class, and is particularly important for scan classes executed by other drivers through the external Tags provider. This property is not used by internal providers. |
Driven Properties
Used by the driven mode to determine when the scan class should run at the fast rate.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Driving Tag | Which Tag will determine when the rate of the scan class should be changed. The Driving Tag should not use this same scan class. The Driving Tag should be on a separate scan class that runs at a faster rate than the Driven scan class. This means that changes to the Driving Tag will be recognized by the system faster, and the change in rate on the Driven scan class will occur faster. |
| Operator | How the Value property should be compared to the Driving Tag's value. If the comparison is true, then the Fast Rate will be used by the Scan Class ,otherwise, the Slow Rate will be used. The Any Change operator works differently than the other operators: The scan class will execute immediately whenever the driving Tag changes value. Using the Any Change operator means that the scan class no longer uses the Slow Rate or Fast Rate properties. |
| Value | Used by the Operator property to determine if the Scan Class should execute at the slow or fast rate. |
| One-shot execution | One-shot will execute once when the comparison condition is true, and not again until the condition become false, and subsequently true. |
Advanced Properties
Settings that subtly affect how the scan class operates.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| OPC Data Mode | This mode dictates how OPC values are obtained. The default mode, Subscription, is preferred because it is much more efficient than a read.
|
| OPC Read After Write | When enabled, a read request will be sent immediately after a write request. This means that the value on the Tag will be updated much quicker to reflect the latest written value. Enabling this property is less efficient as a single write to a Tag becomes two separate requests. This is especially helpful with slower scan classes as the Tags will show the latest value quicker than the normal execution would allow. |
| OPC Optimistic Writes | New in 7.9.2 If enabled, written values will be applied to the OPC Tag immediately. Normally, the system must receive confirmation that a write was successful from the device before the OPC Tag's value would change. This property changes the behavior by assuming the write went through unless the next read value or subscription update proves otherwise. Enabling this will make writes appear to execute much quicker.Works in conjunction with the OPC Optimistic Write Timeout property below. If the OPC Tag does not receive confirmation that the new write was successful within the timeout, the Tag will fallback to the last known value. While in an ambiguous state, the Tag with have a quality of "Good (Provisional)". This setting can be paired with the OPC Read After Write: the Tag will assume the newly written value, while an asynchronous read request is quickly sent out to confirm the write went through. While the write is pending, values received from subscription activities will override the fallback value. Assuming an initial value of 0, if a write of 10 is applied to the OPC Tag, then the Tag will show a value of 10 until the system can confirm the new value. If a subscription update then returns a value of 5, the OPC Tag will fallback to 5. |
| OPC Optimistic Write Timeout | New in 7.9.2 The timeout period for Optimistic Writes. A value of 0 effectively disables the fallback functionality: the new value is maintained on the Tag until the next read or subscription activity. |
Historical Scan Classes
Historical scan classes are simply standard scan classes used by Tags to store history. By using separate scan classes for status and history, it's possible to maintain a Tag's status at a fast rate, without storing large amounts of history unnecessarily.
Despite the fact that there is not a technical differentiation between standard and historical scan classes, it is recommended that you create separate scan classes for each purpose and name them in a manner that indicates their usage. It is common to modify scan classes in order to affect a large number of Tags, and without a consistent distinction it may be possible to affect Tag execution in unexpected ways.
OPC-UA Stale Threshold
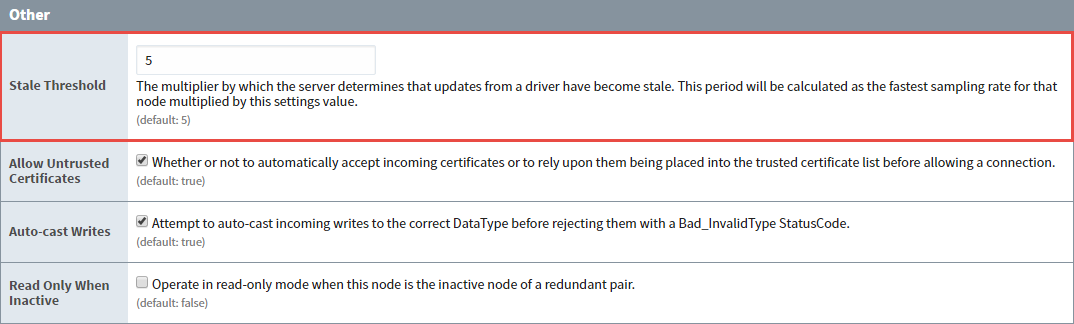
Ignition uses the OPC-UA Stale Threshold setting to determine when updates from a driver have taken too long to complete. This time period will be calculated as the fastest sampling rate for that node multiplied by the Stale Threshold setting value. It's this multiplier on the scan class that determines when the Tag can be marked as stale or not. The default for the Stale Threshold value is set to 5. This is a very important setting because when the network is going slower or the PLC is taking a long time, those Tags need to be marked in Ignition as stale so that the operators know not to trust those values on the screen.
The OPC-UA Stale Threshold is one setting is for the entire Ignition server.
To Edit the Stale Threshold
-
Go to the Configure section of the Gateway, and select OPC-UA Server > Settings.
The Settings page is displayed.
-
Scroll down to the Other section and then to the Stale Threshold setting.
This is a multiplier by which the server determines that updates from a driver have become stale.