Tag Properties
Tags are points of data and may have static values or dynamic values that come from an OPC address, an Expression, or a SQL query. The values can be used on screens and in Transaction Groups. Additionally, Tags offer a core set of features above and beyond simple values, such as scaling, alarming, and history logging. Depending on the specific type of Tag, even more options are available. In general, Tags provide a common interface for tying together many types of data in Ignition.
Tag Configuration in the Designer
Tags are managed in the Tag Editor. To configure a Tag, right-click on it and select Edit Tag. Or create a new Tag by right-clicking on the Tags folder in the Tag Browser and use the New Tag option to select a new Tag type.

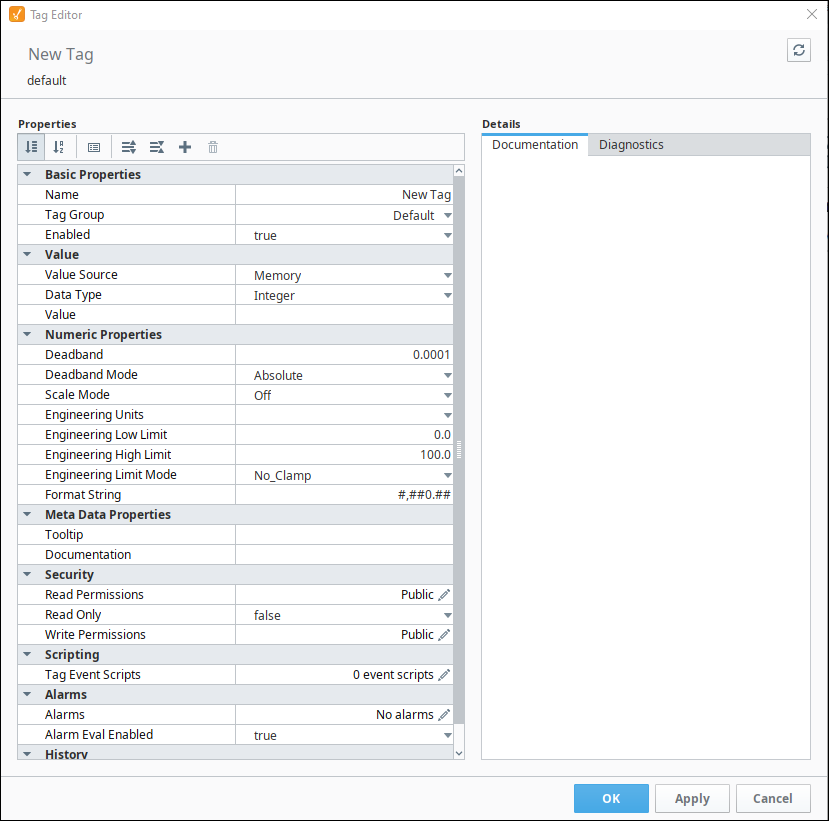
Once the Tag Editor window is displayed you can set the properties for that Tag. The Tag Editor window has the following sections depending on the type of Tag you are creating:
- Basic Properties
- Value
- Numeric Properties
- Meta Data Properties
- Security
- Scripting
- Alarms
- History
Tag Object Types
Some features, such as system.tag.browse, can access the Object Type of the tag (sometimes called "tagType"). Below is a table representing the possible types.
| Tag Object | Type |
|---|---|
| Property | A single value underneath an node. |
| Node | An entity that may have a value and may have children. "Node" is a generic term for other objects in this table, such as a Folder or AtomicTag. |
| Folder | Represented by a folder in the Tag Browser. Folders generally have child nodes, but don't have values or other properties that make up a tag. |
| AtomicTag | A "normal" type of tag. Objects with this type can be one of the following (based on the Value Source property): |
| UdtInstance | An instance of a complex tag instance (UDT Instance). It's important to note that UdtInstances contain other nodes, so this type is generally only seen at the root of a UDT instance.Thus, nodes under a UdtInstance are not considered to have a type of "UdtInstance", unless the child node is actually a UdtInstance: in other words, a nested UDT instance. |
| UdtType | Represents the root of a complex tag definition (UDT Definition). Similar to UdtInstance, nodes under a UdtType have their own object type, so a UdtType represents the root of a complex tag. |
| Provider | Represents a Tag Provider. |
Standard Tag Properties Table
This following table provides detail on each Tag Property, including the binding name, description, data type, and the Tag Types that use the property.
Basic Properties
| Property | JSON/Scripting Name | Description | Data Type | Applicable Tag Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | name | How the Tag will be presented and referenced in the system. The Tag path will be the provider, the folder structure, and this name. | String | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Client, Reference, Memory |
| Tag Group | tagGroup | The Tag Group that will execute the Tag. The Tag Group dictates the rate and conditions on which the Tag will be evaluated. For more details, see Tag Groups. | String | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Enabled | enabled | Whether the Tag will be evaluated by the Tag Group. If false, the Tag will still be present, but will have a bad quality. | Boolean | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
Value
| Property | JSON/Scripting Name | Description | Data Type | Applicable Tag Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value Source | valueSource | Specifies how the Tag determines its value. In other words, sets the type of the Tag (Memory, OPC, Expression, etc). The following lists valid value sources and their JSON Name: | String | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Data Type | dataType | The data type of the Tag. It is important that this be set as correctly as possible with regards to the Tag's underlying data source. The Tag system will attempt to coerce any raw incoming value (for example, from OPC or a SQL query) into the desired type. For detailed information, see Tag Data Types. Click here to see valid values. Note: Regarding Array data types, Alarming, Scaling, and Historical settings applied to an array Tag are propagated down to elements in the array. | String | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Value | value | The value of the Tag. Can only be modified if the Tag allows value writing and the user has sufficient privileges. | Object (depends on the data type of the Tag) | Memory |
| OPC Server | opcServer | Only p resent for OPC Tags. The server against which to subscribe the data point. Only present for OPC Tags. | String | OPC |
| OPC Item Path | opcItemPath | Only present for OPC Tags. The path to subscribe to on the server. The point will be subscribed at the rate dictated by the Tag Group. New in 8.1.5 It's possible to escape curly braces in the item path by using additional curly braces. For example:{{device_name}}would evaluate to{<device_name value>}, allowing you to include braces in the Item Path. | String | OPC |
| Source Tag Path | sourceTagPath | The path to the Tag that this Tag is referencing. Only present for Reference and Derived Tags. | String | Derived, Reference |
| Execution Mode | executionMode | Only present for Query and Expression Tags. Determines how when the Tag executes.
| String | Expression, Query |
| Expression | expression | The expression the Tag will use to determine its value. | String | Expression |
| Read Expression | deriveExpressionGetter | The expression that determines how the value on the Derived Tag is displayed. | String | Derived |
| Query | query | The SQL query to be run, which drives the tag's value. Queries doing database reads and writes are possible, see the Query Type property description for details. | ||
| Write Expression | deriveExpressionSetter | The expression that determines how the value on the Derived Tag is displayed. | String | Derived |
| Datasource | datasource | The database connection that the query Tag will execute against. | String | Query |
| Query Type | queryType | New in 8.1.3 Defines whether the query is executing a database read or a database write. Important for determining the value behavior of the Tag. Possible values are: | String | Query |
Valid Data Type Values
| Data Type | String Value | Integer Value |
|---|---|---|
| Byte | Int1 | 0 |
| Short | Int2 | 1 |
| Integer | Int4 | 2 |
| Long | Int8 | 3 |
| Float | Float4 | 4 |
| Double | Float8 | 5 |
| Boolean | Boolean | 6 |
| String | String | 7 |
| DateTime | DateTime | 8 |
| Text | Text | 10 |
| Byte Array | Int1Array | 17 |
| Short Array | Int2Array | 18 |
| Integer Array | Int4Array | 11 |
| Long Array | Int8Array | 12 |
| Float Array | Float4Array | 19 |
| Double Array | Float8Array | 13 |
| Boolean Array | BooleanArray | 14 |
| String Array | StringArray | 15 |
| DateTime Array | DateTimeArray | 16 |
| Binary Data | ByteArray | 20 |
| Dataset | DataSet | 9 |
| Document | Document | 29 |
Numeric Properties
| Property | JSON/Scripting Name | Description | Data Type | Applicable Tag Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deadband | deadband | A numerical value used to prevent unnecessary updates for Tags whose values change by small amounts. | Numeric | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Deadband Mode | deadbandMode | Defines how the deadband value is used.AbsolutePercent | String | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Scale Mode | scaleMode | If and how the Tag value will be scaled between the source, and what is reported for the Tag. Valid values are as follows:OffLinearSquareRootExponentialFilterBitInversion | String | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Raw Low | rawLow | Start of the "raw" value range. Only present if Scale Mode is set to Linear or Square Root. | Numeric | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Raw High | rawHigh | End of the "raw" value range. Only present if Scale Mode is set to Linear or Square Root. | Numeric | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Scaled Low | scaledLow | Start of "scaled" value range. Raw low will map to Scaled low for the Tag. Only present if Scale Mode is set to Linear or Square Root. | Numeric | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Scaled High | scaledHigh | End of "scaled" value range. Raw high will map to Scaled high for the Tag. Only present if Scale Mode is set to Linear or Square Root. | Numeric | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Clamp Mode | clampMode | How values that fall outside of the ranges will be treated. "Clamped" values will be adjusted to the low/high scaled value as appropriate. Only present if Scale Mode is set to Linear or Square Root. Valid values are as follows:No_ClampClamp_LowClamp_HighClamp_Both | String | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Scale Factor | scaleFactor | For single parameter modes (currently only Exponential Filter), the factor parameter for the equation. Used when the Scale Mode property is set to Exponential Filter | Numeric | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Engineering Units | engUnit | The engineering units of the value. | String | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Engineering Low Limit | engLow | The lowest expected value of the Tag. | Numeric | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Engineering High Limit | engHigh | The highest expected value of the Tag. | Numeric | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Engineering Limit Mode | engLimitMode | Dictates how the engineering range should be enforced on the Tag. If not "Off", the Tag will change to bad quality ("limit exceeded"), when the value falls outside the specified range. Valid values are as follows:No_ClampClamp_LowClamp_HighClamp_Both | Numeric | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Format String | formatString | How the value should be formatted when converted to a string (only applies to numerical data types). Uses # and 0 characters to describe the format. # : If the number in this position is non-zero, then do not show the position. Otherwise, show the number. Useful when you only want to show a decimal position if the value is non-zero. 0 : If the number in this position is non-zero, then show that number. Otherwise, show a zero. Useful to add leading and trailing zeros to a value. See Data Type Formatting Reference. | String | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
Meta Data Properties
| Property | JSON/Scripting Name | Description | Data Type | Applicable Tag Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tooltip | tooltip | The tooltip provides a hint to visual components as to what should be displayed when the user hovers their mouse cursor over the component that is being driven by the value of this Tag. | String | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Documentation | documentation | A freeform text property for information about the Tag. | String | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
Security
| Property | JSON/Scripting Name | Description | Data Type | Applicable Tag Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Read Permissions | readPermissions | Defines the security levels required in order to read values from a Tag. For more information, see Tag Security Properties. Contains the following elements: type): Represents the selected radio button on the security level UI, determining if all of the elements in the securityLevels array are required, or if any of the elements are allowed. Possible values are:
securityLevels): Represents allowed security levels for this permission. Each level is represented as a JSON object, containing a "name" value that represents the name of a security level, and a "children" array which represents any levels under the current. The actual "selected" levels are any levels that have an empty "children" object. | JSON Object | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Read Only | readOnly | Defines whether a Tag is read-only or writeable. For more information, see Tag Security Properties. | value: boolean | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Write Permissions | writePermissions | Defines the security levels required in order to read values from a Tag. For more information, see Tag Security Properties. Contains the following elements:type): Represents the selected radio button on the security level UI, determining if all of the elements in the securityLevels array are required, or if any of the elements are allowed. Possible values are:
securityLevels): Represents allowed security levels for this permission. Each level is represented as a JSON object, containing a "name" value that represents the name of a security level, and a "children" array which represents any levels under the current. The actual "selected" levels are any levels that have an empty "children" object. | JSON Object | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
Read Permissions JSON Example
The JSON in this example uses the configuration shown in the image below. Permission is granted if the security levels on the request are from either an "Administrator" user, or if the request originated from the "Zone A" Security Zone.

"readPermissions": {
"type": "AnyOf",
"securityLevels": [
{
"name": "Authenticated",
"children": [
{
"name": "Roles",
"children": [
{
"name": "Administrator",
"children": []
}
]
}
]
},
{
"name": "SecurityZones",
"children": [
{
"name": "Zone A",
"children": []
}
]
}
]
}
Write Permissions JSON Example
The JSON in this example uses the configuration shown in the image below. Permission is granted if the security levels on the request are from either an "Administrator" user, or if the request originated from the "Zone A" Security Zone.

"writePermissions": {
"type": "AnyOf",
"securityLevels": [
{
"name": "Authenticated",
"children": [
{
"name": "Roles",
"children": [
{
"name": "Administrator",
"children": []
}
]
}
]
},
{
"name": "SecurityZones",
"children": [
{
"name": "Zone A",
"children": []
}
]
}
]
}
Scripting
| Property | JSON/Scripting Name | Description | Data Type | Applicable Tag Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tag Event Scripts | eventScripts | Each Tag has the option to have Tag Event Scripts on it. When you edit a Tag, you can navigate to the Tag Events screen to see a list of all of the Tag scripts. You can then select which event you would like to write a script for. You can even write a script for multiple events if you like. For detailed information, see Tag Event Scripts. When interacting with a Tag from a script, the Tag Event Scripts are represented as an array of JSON objects.Key Description:qualityChangedvalueChangedalarmActivealarmClearedalarmAcked | JSON Array | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
Alarms
| Property | JSON/Scripting Name | Description | Data Type | Applicable Tag Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alarms | alarms | Tags have the ability to define any number of alarms. Each alarm is a condition that will be evaluated when the value of the Tag changes. When the condition becomes true, the alarm is said to be active. When it becomes false, the alarm is said to be cleared.For detailed information, see Tag Alarm Properties. | JSON Array of JSON objects. For detailed information, see Tag Alarm Properties. | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Alarm Eval Enabled | alarmEvalEnabled | Determines if alarms will be evaluated on this tag. | Boolean | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
History
| Property | JSON/Scripting Name | Description | Data Type | Applicable Tag Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| History Enabled | historyEnabled | Whether the Tag will report its history to the Tags Historian system. | Boolean | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Storage Provider | historyProvider | Which Tag Historian data store the Tag will target. A particular Tag can only target one history store. For more information, refer to History Providers on the Tag History Gateway Settings page. | String | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Deadband Style | historicalDeadbandStyle | There are three styles to choose from: Auto, Analog, or Discrete.When set to Auto, this setting will automatically pick from Analog or Discrete, based on the data type of the Tag.AutoAnalogDiscrete | String | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Deadband Mode | historicalDeadbandMode | Defines how the deadband value is used.Absolute) - The deadband setting is considered to be an absolute value. | String | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Historical Deadband | historicalDeadband | A deadband that applies only to historical evaluation. | Numeric | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Sample Mode | sampleMode | Determines how often a historical record should be collected.OnChange) - Collects a record whenever the value on the Tag changes.Periodic) - Collects a record based on the Sample Rate and Sample Rate Units properties.TagGroup) - Collects a record based on the Tag Group specified under the Historical Tag Group property. | String | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Sample Rate | historySampleRate | When the Sample Mode property is set to "Periodic", this property (working in conjunction with the Sample Rate Units property) determines how often a record should be collected. | Numeric | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Sample Rate Units | historySampleRateUnits | When the Sample Mode property is set to "Periodic", this property (working in conjunction with the Sample Rate property) determines the unit of time that will be use in record collection.MSSECMINHOURDAYWEEKMONTHYEAR | String | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Historical Tag Group | historyTagGroup | When the Sample Mode property is set to "Tag Group", this property determines which Tag Group will be used to collect records. | String | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Min Time Between Samples | historyTimeDeadband | Minimum time between records. Useful in restricting the number of records collected when the Sample Mode is set to "Tag Change". Prevents multiple consecutive Tag changes from triggering consecutive record collections. Works in conjunctions with the Min Time Units property. The Value is calculated off of the value timestamp. | Integer | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Min Time Units | historyTimeDeadbandUnits | Units of time to use with the Min Time Between Samples property.MSSECMINHOURDAYWEEKMONTHYEAR | String | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Max Time Between Samples | historyMaxAge | Maximum time between samples. Works in conjunction with the Max Time Units property. If a sample has not been collected by the time range specified by these two properties, then a record will be collected on the next sample interval.Note: This setting will be ignored if the Sample Mode is set to Tag Group, and the targeted Tag Group is using non-default values for its Max Time Between Samples setting. The implication being that non-default values on the Tag Group settings take precedence over this setting. | Integer | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
| Max Time Units | historyMaxAgeUnits | Maximum time in units is defined as: Milliseconds, Seconds, Minutes, Hours, Days, Weeks, Months, and Years.MSSECMINHOURDAYWEEKMONTHYEAR | String | OPC, Query, Expression, Derived, Reference, Memory |
Runtime Properties
In addition to properties listed in the Tag Editor, some properties are exposed as runtime properties in the Tag Browser. These properties are valid targets for component bindings and tag reads/writes.
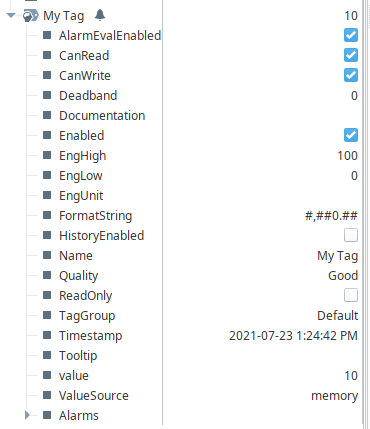
Most runtime properties are representations of properties that can be configured in the Tag Editor. However there are some properties only listed in the Tag Browser:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| CanRead | New in 8.1.8 A read-only property that represents whether or not this tag can be read from the current security context. This is determined by looking at the read permission settings on the tag and the tag provider's permission settings. |
| CanWrite | New in 8.1.8 A read-only property that represents whether or not this tag can be written to from the current security context. This is determined by looking at the write permission settings on the tag, the Read Only property, and the tag provider's permission settings. |
Custom Tag Properties
Custom Tag properties allow application designers to configure their own properties on Tags to store unique values on any Tag. Once added, a custom property can be referenced like any other Tag property via bindings, expressions, and scripts.
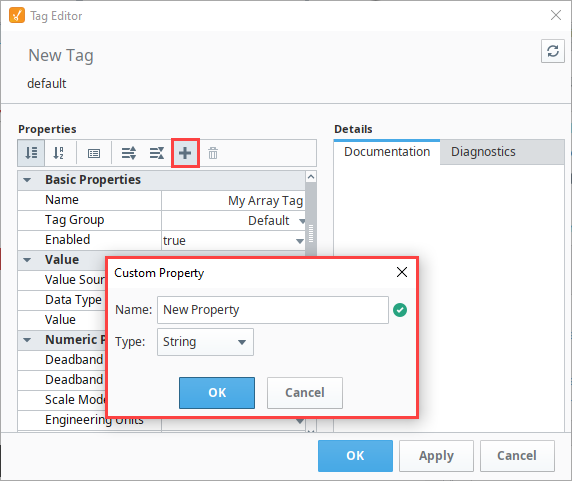
Both the Perspective and Vision visualization systems can bind to custom properties. In the following example, we already have Array Tag. Now let's add a custom property.
-
Open an existing Tag and click on the Add
icon in the Tag Editor.
-
This opens the Custom Property dialog box. Enter a Name for your Tag, select the Data Type, and click OK.
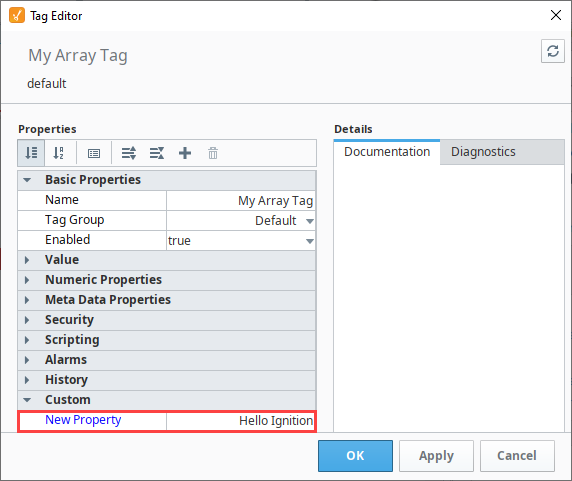
-
Scroll down to the bottom of your Tag properies and you'll see your Custom Property. We added the value "Hello Ignition".
-
When you open your Tag Browser and expand the My Array Tag, you'll see your Custom Property.

Vision Client Tags
Client Tags have the ability to be used as either Expression or SQL Query Tags. There is an Expression/SQL page in the Tag editor that allows you to select what type it is.
Query/Expression Attributes
| Property | Binding/Scripting Name | Description | Data Type | Applicable Tag Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPC Server | OPCWriteBackServer | The server against which to subscribe the data point. | String | Query, Expression |
| OPC Item Path | OPCWriteBackItemPath | The path to subscribe to on the server. | String | Query, Expression |
| Query | Expression | Text area to build your query or expression. | String This is the code used by the Tag: either a SQL Query for Query Tags, or an Expression for Expression Tags. | Query, Expression |
| Query Type | QueryType | When the TagType property is set to 1, this property determines if the Tag should be a Memory, Expression, or Query Tag. | IntegerSupported tag types and their integer values include: | Query, Expression, Memory |
| Datasource | SQLBindingDatasource | The default data source of the Tag provider. | String | Query |