History Providers
The Historian Core module supports multiple storage backends through a system of history providers. Each provider manages its own storage configuration and database schema, allowing you to log tag history in different ways depending on your system’s needs. You can configure and manage history providers on the Services > Historians > Historians page on the Gateway.
Providers range from lightweight embedded engines to external SQL databases and remote Gateways. This flexibility lets you balance performance, scalability, and redundancy. Each provider type has unique behaviors, storage formats, and limitations. For technical details on the underlying storage schemas, see the Ignition Database Table Reference.
⚠️ 8.3 Known Issue
If you are storing history data to a remote Gateway, and the remote Gateway is disabled, there will be a flood of messages written to the log. For a full list of known issues, click here to learn more.
For automation or custom tooling, you can use the system.historian scripting functions to interact with history providers programmatically.
Creating a History Provider
Most provider types must be created manually. To create a new provider, complete the steps below.
- Go to Services > Historians > Historians on the Gateway.
- Click Create Historian.
- Select a historian type and click Next.
- Enter a name and configure the settings.
- Click Create Historian to finish.
CSV Historian
The CSV Historian imports historical data from a CSV file. This provider is read-only and does not support realtime tag history storage.
Settings
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Specifies the unique name used to identify the historian provider. |
| Description | Provides an optional user-defined description for the provider. |
| Enabled | Set whether this historian is enabled or disabled within the Gateway. |
| File Path | Specifies the CSV file path. Required format: timestamp column followed by value columns, with tag names defined in the header row. |
| Relative Timestamps | When enabled, treats the first timestamp as a reference point, interpreting subsequent timestamps as relative offsets from this initial time. |
Historian Splitter
The Historian Splitter writes tag history to two configured providers simultaneously. This configuration is useful for redundancy, system migrations, or archiving data in multiple locations. When querying history, results are typically returned from the first provider, unless limits are configured.
Settings
Main
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Specifies the unique name used to identify the historian provider. |
| Description | Provides an optional user-defined description for the provider. |
| Enabled | Set whether this historian is enabled or disabled within the Gateway. |
Storage
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| First Connection | Data is stored to both connections equally. However, all queries execute against the first connection, unless a limit is imposed using the settings below, or the first connection is unavailable. |
| Second Connection | Specifies the secondary history provider. Data is written here alongside the first connection, but this provider is not queried unless query limits are applied or the first connection fails. |
Querying
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Limit First Connection Query | If enabled, restricts query operations to a specific time window on the first provider. |
| Limit Length | Defines the size of the time window applied when query limits are enabled. |
| Limit Units | Specifies the time units for the limit window (e.g., minutes, hours, days). |
DB Table Historian
The DB Table Historian enables Ignition to read historical data from external or custom-managed SQL tables using a flexible path syntax. This type is read-only and is commonly used for integrating third party or legacy historical datasets into Ignition’s trending and reporting tools.
Because this provider requires mapping raw SQL tables into a format Ignition can interpret as tag history, setup is more involved than with other historian types. You'll need to configure column mappings, timestamp fields, and optional filters using specialized historian paths.
See the DB Table Historian Provider page for details.
Core Historian
The Core Historian is an embedded, high-throughput time-series database using QuestDB. The Core Historian supports partitioning, deduplication, archiving, and native aggregation.
The Core Historian writes directly to disk using a high-performance write-ahead log (WAL) system. It does not use Store and Forward, so it bypasses the buffering and retry mechanisms used by other historian types.
See the Core Historian page for more details.
Internal Historian (Legacy)
The Internal Historian (Legacy) is a lightweight embedded historian that uses a local SQLite database. It is well-suited for Edge devices, standalone installations, or small systems that require basic history storage without the overhead of an external database. This provider supports automatic data pruning and remote synchronization to another Gateway.
SQLite-based historians do not record scan class execution data.
Settings
Main
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Specifies the unique name used to identify the historian provider. |
| Description | Provides an optional user-defined description for the provider. |
| Enabled | Set whether this historian is enabled or disabled within the Gateway. |
Limits
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Time Limit Enabled | If enabled, old data will be pruned based on its age. |
| Time Limit Size | Specifies how long data should be retained before it is pruned. |
| Time Limit Units | Sets the time unit (e.g., Days, Weeks) used for the time-based limit. |
| Point Limit Enabled | If enabled, data will be pruned once a specified number of records is reached. |
| Point Limit Size | Defines the maximum number of data points the historian will store. |
Sync Settings
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote Sync Enabled | Enables the provider to sync history data to a remote Gateway. |
| Remote Gateway Name | The Gateway to target for remote synchronization. The Historian Core module must be installed, and allow remote storage. |
| Remote Provider Name | The remote history provider to sync data to. |
| Sync Frequency | The frequency with which data will be sent to the remote Gateway. This setting will be used in conjunction with the sync schedule, if enabled. |
| Sync Frequency Units | Sets the unit of time (e.g., seconds, minutes) used for sync frequency. |
| Max Batch Size | The maximum number of data points that will be sent per batch to the remote Gateway. |
| Enable Schedule | If enabled, the data will only be synchronized during the times specified by the pattern provided. |
| Schedule | A comma separated list of time ranges (e.g., 9:00-15:00). |
Metadata Storage
When enabled on a tag, metadata is stored automatically in system-managed tables. This includes properties like tag path, data type, units, and scaling. Metadata is preserved even if the tag is removed.
Metadata must be explicitly enabled in the Tag Editor by setting Include Metadata to true. This setting is found in the History section when editing a tag in the Designer.
OPC HDA Historian
The OPC HDA Historian connects to OPC HDA (Historical Data Access) servers to read historical tag data. This provider is supported only on Windows systems and requires the OPC COM module to function. It is a read-only provider and cannot store or forward tag history.
This provider cannot write tag history.
Settings
Main
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Specifies the unique name used to identify the historian provider. |
| Description | Provides an optional user-defined description for the provider. |
| Enabled | Set whether this historian is enabled or disabled within the Gateway. |
Server
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection Type | Select either a local or remote connection type. |
| Provider | Each OPC server is identified by a "progid". This is the name that will be used to connect to the server. |
| Use Flat Browsing | Flat browsing returns all items at once. This is less efficient than normal browsing, but if a server only supports flat browsing, select this option. |
Remote Historian
The Remote Historian provider connects to another Ignition Gateway over the Gateway Network to read from or write to a remote history provider. This allows distributed storage or centralized access to tag history across Gateways.
Settings
Main
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Specifies the unique name used to identify the historian provider. |
| Description | Provides an optional user-defined description for the provider. |
| Enabled | Set whether this historian is enabled or disabled within the Gateway. |
Remote Gateway
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Gateway | Specifies the name of the remote Gateway to connect to. |
| Provider | Specifies the name of the history provider on the remote Gateway. |
Storage
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Storage Allowed | If false, the provider will only be used for querying historical data. If true, the provider will create a store and forward pipeline for sending data to a remote Gateway. |
| Max Group Size | The maximum number of data points that can be sent per request. This value is used in conjunction with the store and forward settings to dictate how much data is sent at once. (0=unlimited) |
Simulator Historian
The Simulator Historian generates simulated tag history data for use in testing, training, and demonstration environments. It allows you to visualize trends, test charts and bindings, and experiment with history queries all without needing a live system or real tag activity.
See the Simulator Historian page for more info.
SQL Historian
The SQL Historian stores tag history in an external SQL database such as MySQL, SQL Server, or PostgreSQL. It supports advanced features like partitioning for performance, pruning for data retention, stale value detection, and summary table generation through pre-processed partitions. This provider is well-suited for systems that require robust reporting, integration with external tools, or long-term historical data storage.
The SQL Historian module is required in addition to the Historian Core module for this history provider to be listed on the Gateway.
Settings
Main
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Specifies the unique name used to identify the historian provider. |
| Description | Provides an optional user-defined description for the provider. |
| Enabled | Set whether this historian is enabled or disabled within the Gateway. |
| Data Source | Identifies the database connection used to store historical data. |
Data Partitioning
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable Partitioning | Enables time-based table partitioning to segment historical data. Partitioning improves query performance and simplifies data lifecycle management. |
| Partition Length | Specifies the duration of each partition (e.g., 1, 7, or 30). |
| Partition Units | Defines the unit of time for each partition (e.g., Days, Weeks, Months). |
| Enable Pre-processed Partitions | Pre-processed partitions will use more space in the database, but can improve query speed by summoning data, reducing the amount that must be loaded. |
| Pre-processed Window Size (seconds) | When the pre-processed partitions property is enabled, this setting defines the window size. Configuring this setting has a direct impact on whether or not the pre-processed data will be used for tag history queries. If the query window size is greater than the pre-processed window size, then the pre-processed tables are used instead of the raw data tables. If the query window size is less than the pre-processed window size, then the raw data table is used. Default is 60 seconds. |
Data Pruning
Data pruning works by deleting old partitions. Therefore, data will only be removed when a partition has no data younger that the prune age.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable Data Pruning | Data will be deleted after the specified time period. |
| Prune Age | Specifies the maximum age of data to retain in the database. |
| Prune Age Units | Defines the units of time used to interpret the prune age. |
Advanced
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable Stale Data Detection | If enabled, tracks tag group executions to determine the difference between unchanging values, and values that are flat due to the system not running. |
| Stale Detection Multiplier | The multiplier for tag group rate used to determine when values are stale. If tag group execution is not recorded within this amount of time, values will be considered bad on query. |
Pre-Processed Partitions
Pre-processed partitions are used to aggregate data partitions into smaller, more efficient partition tables. When enabled, the system will use the pre-processed window size (in seconds) and summarize the raw historical data into blocks of this size. For example, if a tag was logged to the database every second, a window size of 60 seconds will summarize the 60 records logged into a single, much smaller set of records in the pre-processed table. On large systems with millions of historical records per month, this summarization of data can result in much smaller data partition tables that are more efficient to query.
When SQL-based history providers opt into pre-processed partitions, records stored by the provider are stored in two different sets of partitions: the normal partitions and a summarized pre-processed partition. In other words, a new partition table is created to store the pre-processed records. The pre-processed partitions use the following naming convention: sqlth_data_X_YYYY_MM_windowSize, where X is the provider driver ID from the sqlth_drv table. While this takes up more space in the database, it can improve query speeds by dramatically reducing the amount of resulting data points.
Pre-processed partitions are only used under specific conditions:
- When querying through legacy scripting functions such as system.tag.queryTagHistory and system.tag.queryTagCalculations.
- When the requested query interval exceeds the configured Pre-processed Window Size.
For example, if the Pre-processed Window Size is set to 60 seconds, and a legacy query requests intervalSeconds=90, the query engine will retrieve data from the pre-processed partitions instead of the raw history tables, resulting in faster queries and smaller result sets. If the query uses a smaller interval (e.g., 30 seconds), the raw data tables are used instead.
The system.historian.queryRawPoints function does not leverage pre-processed partitions. Queries made through this function always access raw history data, even if pre-processing is enabled.
The Resultset 1 table below shows the normal partitions of 50 raw values between a highlighted time block spanning from 12:12:03.52 to 12:13:03.52.
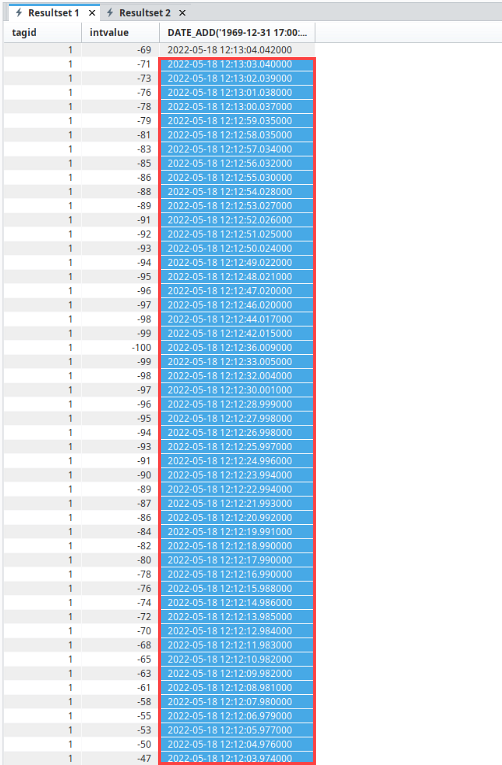
With pre-processed partitions enabled, these 50 rows of data were also summarized into four rows shown on the Resultset2 tab displaying the pre-processed partition values.
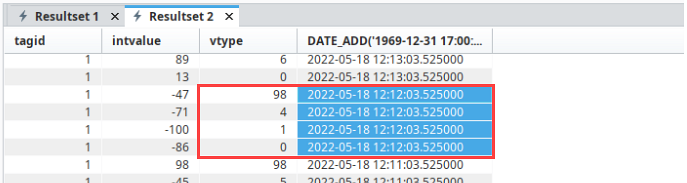
You may notice that the pre-processed partition table also includes a vtype column. The vtype represents metadata about the record using the following flags:
- 0: Time-weighted average
- 1: Minimum value
- 2: Maximum value
- 4: Exit value (last in window)
- 32: First value flag (used with min/max to indicate which came first)
- 64: Entry value (first in window)
Each record in the set represents a different value for that 1 minute time window, each value given a different vtype. The first record above has a vtype of 98, which means that this record represents the entry (64), the first value (32), and the max (2) of the records between 12:12:03.52 and 12:13:03.52. The second record value is 4. This value represents the exit value for this same 1-minute time block. The third record value is 1, which represents the min value. Finally, the last record value is 0, which represents the direct average for the original 50 rows.
For more details on table structure, see the Ignition Database Table Reference.