Omron NJ Driver
Connect Ignition to an Omron NJ Device
-
Go to the Config section of the Gateway Webpage.
-
Scroll down and select OPC UA > Device Connections.
-
On the Devices page, click on Create new Device.
-
Select Omron NJ Driver, and click Next.
-
On the New Device page, leave all the default values and type in the following fields:
- Name: Omron
- Hostname: type the IP address, for example 74.125.224.72
- Check the box for Show advanced properties? to see the additional settings, but you can keep all the defaults.
-
Click Create New Device. The Devices page is displayed showing the Omron device is successfully created and added to Ignition.
-
On the Devices page, click the Tags link next to the newly created device. The Manage Tags page is displayed, allowing you to configure which variables in the device will show up as Tags in Ignition.
Device Settings
General
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Device name. |
| Description | Description of the device connection. |
| Enabled | Default is set to true. |
Main
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Hostname | The IP Address of the device. |
| Local Address | New in 8.1.8 The local address to connect from when establishing a TCP connection. If left blank, then the driver will simply pick an available address. |
| Timeout | The request timeout, specified in milliseconds. The default is 2,000. |
| Concurrency | The number of concurrently issued requests allowed. There is a 1:1 correlation between concurrency and the number of CIP connections used. The default is 2. |
Advanced
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection Size | The CIP connection size to use. The default (and maximum) is 1,994 bytes. |
| Date/Time Offset | New in 8.1.1 Offset in hours for Date/Time values. Default is 0. The driver needs an advanced setting for an offset to be applied when reading or writing date/time values. |
| Slot Number | The slot number in the backplane in which the CPU is located. The default is 0. |
Exporting from the Device
To export variables from Sysmac Studio, navigate to the global variables and select Tools > Export Global Variables > CX-Designer.
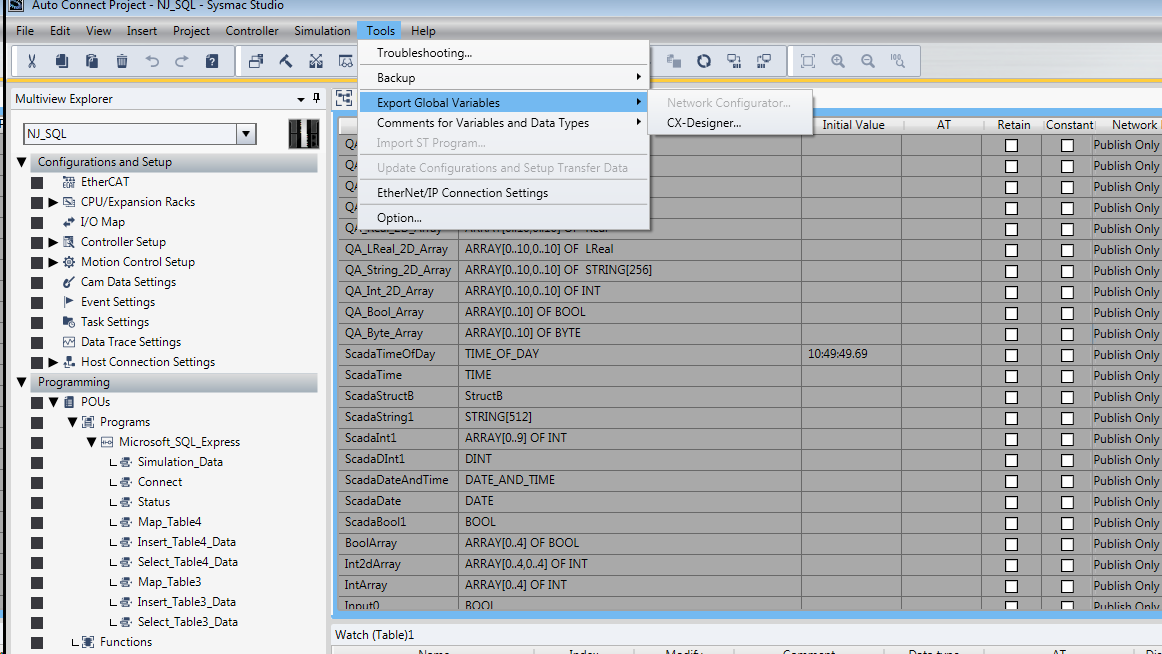
The variables will be saved to the clipboard in tab-separated format. You can now paste the contents into an empty text file for use with importing into the Ignition Gateway.
Managing Tags
In order to browse Tags in the Designer, you must first create a mapping for the device in the Gateway. The Manage Tags page can be accessed by navigating to the Omron device and clicking the addresses link.
Importing Tags
Once on the Manage Tags page, you can manually enter the Tags, or import them from a tab-separated file. When importing, first choose a file, then click the Load Configuration File button to append Tags to the table.

Once you save any changes made to the Tag mapping, you can view the Tags in the Connected Devices window of the Designer.
Addressing
In the Tags table of the Manage Tags page, we have four columns of configuration per Tag:
- Browse Name - The corresponding address of the variable found in the Omron device. Struct members are separated with periods.
- Datatype - The datatype of the variable found in the Omron device.
- Chars - The maximum number of characters that a String Tag will contain.
- Elements - Denotes whether the Tag is considered a scalar or array. See below for more detail on specifying the number of elements to read from the device.
- R/W - Specifies read / write access permissions on the Tag.
Support for the following data types is included:
- TIME_NSEC
- DATE_NSEC
- TIME_OF_DAY_NSEC
- DATE_AND_TIME_NSEC
Scalars
Leaving the Elements column blank will result in a scalar Tag. When reading from the device, only one element will be requested.
Arrays
Specify the number of elements in an array in the form of 0..N. The initial index 0 is always included, so an array mapped with 0..9 elements is a 10 element array.
Array elements may also be specified with a single integer representing the last offset. For example, an integer value of 5 is equivalent to 0..5.
The number range specified in the Elements field can deviate from the range specified in the device's program. Thus, if an array was configured with a range of 0 - 4, but the mapping on the Ignition Gateway is set to 3 - 7, then the resulting items would be offset as follows:
| PLC Program | Tag in Ignition |
|---|---|
| 0 | BoolArray_3_ |
| 1 | BoolArray_4_ |
| 2 | BoolArray_5_ |
| 3 | BoolArray_6_ |
| 4 | BoolArray_7_ |
This is because the driver always assumes that the lowest configured element on the mapping page matches up with the lowest element in the PLC program. As seen above, this can cause some confusion if the mapping on the Ignition Gateway is configured with a different range.
For this reason, it is highly recommended to configure the Elements field on the Ignition Gateway to match the range used in the PLC program.
Note, that this also applies to Multidimensional Arrays.
Multidimensional Arrays
Multidimensional arrays are specified in the same way as arrays with each group of indices separated by a comma. For example, entering 0..3,0..3 into the Array Elements field specifies two groups of indices.
Strings
The number of characters for String variables is specified in the Chars field. String arrays are mapped using both the Chars and Elements fields.